cara menyambungkan wifi ke laptop windows xp

Title: Cara Memperbaiki Wifi Tidak Bekerja Di Windows XP Tutorial
Channel: MDTechVideos International
Cara Memperbaiki Wifi Tidak Bekerja Di Windows XP Tutorial by MDTechVideos International
cara menyambungkan wifi ke laptop windows xp, cara enable wifi di laptop, cara connect wifi ke pc windows 10
Windows XP WiFi Connection: The SHOCKINGLY Easy Fix!
Windows XP WiFi: Unlocking the Wireless World (Surprisingly Simple!)
Remember the days of Windows XP? Ah, the nostalgia! The operating system felt groundbreaking then. However, setting up WiFi on XP could sometimes feel like navigating a minefield. But fear not, because a shockingly easy fix exists!
The WiFi Riddle: Initial Hurdles and Headaches
Initially, getting WiFi working on Windows XP was often a trial. We faced challenges like outdated drivers and confusing settings. Consequently, many users wrestled with network configurations. Finding the correct settings felt like solving a puzzle. The process often became incredibly frustrating. You probably remember wrestling with cryptic error messages. Sadly, the lack of intuitive interfaces didn't help matters either. So, many people simply gave up.
Hunting Down the Right Driver: The First Step
First, you need the correct drivers. These are software components that allow your network adapter to communicate. Finding the right driver remains essential for success. Where do you start? Begin by identifying your network adapter's model. Consult the device's documentation or the manufacturer's website. Next, download the appropriate driver package. Ensure the driver is compatible with Windows XP. Downloading from trusted sources is crucial. Therefore, avoid suspicious websites. You should always scan downloaded files for malware.
Installing the Driver: A Smooth Transition
Installing the driver is the next stage. After downloading, run the setup executable. Follow the on-screen instructions. The process typically involves agreeing to terms and conditions. The system will then guide you through the steps. Afterwards, you might need to reboot your computer. However, a reboot isn't always needed. Pay close attention to any prompts during installation.
Configuring Your Wireless Connection: Taking Control
Now for the fun part: configuration. Your network adapter is now ready. Now, access your network connections. You will find this in the Control Panel. Choose "Network and Internet Connections." Then, select "Network Connections." A list of available networks will appear. If your WiFi network is visible, select it. Double-click to configure the connection. You'll likely need your network's security key. Make sure you have it readily available.
Security Protocols: Understanding WEP, WPA, and WPA2
Understanding security protocols is also extremely important. This helps protect your connection. Windows XP supports older protocols like WEP. Nevertheless, WEP is not very secure. The preferred options are WPA or WPA2. These offer superior encryption. So, choose WPA2 if your router and adapter support it. This ensures the best security. Enter your network's security key. Now, proceed to connect.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Fixing Problems Quickly
Encountering problems is common. Don't panic! Let's consider some common issues. First, double-check your network key. Typos are prevalent causes of connection failure. Verify that your router is broadcasting its SSID. Also, your network's name must be visible. Make sure your drivers are up-to-date. Consider updating your drivers from the Device Manager. There, you can check for updates. Is your wireless adapter enabled? Check the Network Connections panel. Ensure the adapter is activated.
Connecting to the Internet: Riding the Digital Wave
If all goes well, you’ll be online. Now you are free to explore the internet. Celebrate your successful WiFi setup. You can now browse the web and check your email. You can also download software and stream content. This moment is incredibly rewarding! Finally, you’re connected!
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Configurations
Beyond the basics lie advanced configurations. For example, you can set a static IP address. You can also customize DNS settings. These advanced settings can optimize your network performance. Yet, these are usually not necessary. If you are experiencing issues, consider these advanced settings. For most users, however, the default settings should suffice.
Windows XP and WiFi: Still Viable Today?
Windows XP has become an old operating system. Nevertheless, many of you still use it for various reasons. WiFi is still completely usable. The process may be a little more involved. Yet, you can definitely enjoy the benefits of wireless connectivity. You could even use a modern USB WiFi adapter. This would bring more modern WiFi standards.
Embracing the Digital Frontier: Concluding Thoughts
Connecting to WiFi on Windows XP may require some effort. But it's definitely achievable. By following the guidance above, you should be able to unlock the wireless world. Consequently, you can enjoy the digital age on your XP system. With a little patience, you can conquer this task. So, go forth and connect!
Unlock FREE WiFi: Download the Hotspot App NOW!Let's dive in!
Windows XP WiFi Connection: The SHOCKINGLY Easy Fix!
Ah, Windows XP. The operating system that brought us Clippy, dial-up internet, and a whole lot of nostalgia. But let's be honest, getting your ancient laptop, or that trusty desktop tucked away in the attic, connected to the WiFi can feel like trying to decipher hieroglyphics. We've all been there, staring at that network icon, feeling like we're about to pull our hair out. But guess what? It's actually shockingly easy to get Windows XP back online. Prepare to be amazed!
1. The WiFi Wilderness: Why XP Can Be a Nightmare (and Why We're Here to Help)
Think of it like this: Windows XP is a seasoned traveler, a bit set in its ways, and doesn’t always understand the modern, fast-paced world of WiFi. New security protocols, fancy routers…it all feels like a foreign language. That’s where we come in. We're your guide, the sherpa to help you navigate the WiFi wilderness. We've battled this beast, and we're here to share the spoils.
2. Before We Begin: The Must-Haves You’ll Need
Before we jump into the deep end, let's make sure we have what we need. Think of it as packing your survival kit:
- A Windows XP Machine: Obviously! This is the star of the show.
- A Wireless Network Card: Hopefully, your machine already has one built-in (usually present in laptops). If not, you'll need a compatible wireless adapter. You can get these as USB dongles or internal cards.
- Your WiFi Network Name (SSID) and Password: Keep these handy. They're your key to the wireless kingdom.
- Patience: (Just kidding…sort of!) We’ll make this as painless as possible.
- An active internet connection (through another device initially): This isn't strictly necessary, but helpful for grabbing software updates.
3. Finding Your WiFi Card: Is it Even Present?
Okay, first things first: Is your computer even seeing your WiFi card? Here's the easiest way to check:
- Look in the System Tray: The area in the bottom right corner of your screen, near the clock. Do you see a little network icon that looks like a computer screen with a signal strength symbol? If yes, great! If not…don't panic yet!
- Check Device Manager: This is where Windows keeps track of all your hardware. Click “Start,” right-click on “My Computer” or “Computer,” and select “Manage.” Then, in the left-hand panel, click "Device Manager."
- Expand "Network adapters." Do you see your WiFi card listed? It might be labeled something like "Wireless Network Adapter" or "802.11b/g/n Wireless LAN Card."
- If you see a yellow exclamation mark next to your WiFi card, it means there's a driver issue. More on that later!
- If you don't see your WiFi card, it could be disabled (check your laptop’s physical switch if it has one) or not installed properly.
4. The Driver Dilemma: The Silent Killer of WiFi
Drivers are the software that allows your Windows XP machine to "talk" to your WiFi card. Think of them as a translator. Without the right translator, your computer and WiFi card will be speaking different languages.
- The Problem: Many newer WiFi cards aren't officially supported by Windows XP. You might need to track down older drivers.
- The Solution:
- Check the Manufacturer's Website: Go to the website of your WiFi card's manufacturer (e.g., Intel, TP-Link, Netgear) and look for drivers for your specific card model.
- Use the Hardware ID: Go back to Device Manager (explained above). Right-click on your WiFi card, select "Properties," and go to the "Details" tab. In the "Property" dropdown, select "Hardware Ids." Copy the long string of text it displays. Search for this online. This often leads you to the right driver.
- Driver Pack Solutions: These collections of drivers can sometimes get the job done, too, (use with caution and run a virus scan before).
5. Installing the Driver: Making the Connection Possible
Once you've downloaded the right driver:
- Run the Installer: Double-click the driver's setup file and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Restart Your Computer: This is crucial! The computer will not work without the restart.
6. The Wireless Configuration Wizard: Your XP WiFi Sidekick
Windows XP has a built-in wizard to help you connect to WiFi networks.
- Open the Wizard: Double-click on the network icon in the system tray. If you completed the previous steps correctly, you should see a list of available networks.
- Select Your Network: Choose your network from the list and click "Connect."
- Enter Your Password: Type in your WiFi password. Make sure "Connect even if the network is not broadcasting its name (SSID)" is unchecked unless you have a hidden network.
- Enjoy Your Internet!
7. Troubleshooting Common Issues: When Things Go Wrong
Sometimes, even with the right drivers and a wizard, things can go wrong. Here's a quick cheat sheet for common problems:
- "Unable to connect to the network": Double-check your password, make sure your router is broadcasting the network name (SSID), and move closer to the router.
- Slow Internet Speeds: This could be due to a weak signal. Try moving closer to the router. Also, remember how old the hardware is.
- Limited or No Connectivity: Make sure the router isn't blocking your computer's MAC address. Check your router's manual.
8. Security Considerations: Protecting Your Vintage Machine
Connecting an older operating system like Windows XP to the internet requires extra vigilance. It's like driving a classic car: while charming, it might not have the latest safety features.
- Use a Firewall: Ensure Windows Firewall is enabled.
- Update Antivirus Software: Make sure your antivirus program is up to date. This is crucial.
- Consider a Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, adding an extra layer of security.
- Be Careful What You Click: Think of the internet as a busy street. Always be cautious, especially when surfing the internet.
- If Possible Use a Second Device: Test or verify connectivity on a machine with better security.
9. The WEP/WPA Dilemma: Security Protocols Explained (Simplified)
Modern routers use security protocols like WPA2 or WPA3, whereas Windows XP's capabilities might be more limited.
- WEP: Older and less secure (avoid it if possible).
- WPA/WPA2: More secure. Your router should be set to WPA2 if possible. If your XP machine struggles, you might have to configure it to WPA.
- How to Check Your Router's Security: Log into your router's settings (usually by typing its IP address into your web browser - check your router's manual for instructions). Look for the "Wireless Security" or "Security" settings.
10. Hidden Networks: Finding the Invisible WiFi
If your network is hidden (not broadcasting its SSID), you'll need to enter the network information manually.
- In the Wireless Configuration Wizard: When the list of available networks appears, click on "View Wireless Networks." Then, click “Change the order of preferred networks.” Click "Add". Enter your network name (SSID), security type (WPA, WEP, etc.), and password.
11. The Static IP Conundrum: A Rarely Needed Fix
In rare cases, your router might require your computer to have a static IP address.
- Go to Network Connections: Click "Start," then "Control Panel," then "Network and Internet Connections," then "Network Connections." Open the properties for your wireless network connection.
- Change the Protocol: Select "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)" and click "Properties."
- Specify the IP Address: Click "Use the following IP address" and enter the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information provided by your router (or your internet service provider).
12. Updating Windows XP: A Lost Cause? (But Still Potentially Helpful)
While Microsoft ended support for Windows XP ages ago, some security updates might still be available unofficially.
- Use with Extreme Caution: These updates are not officially supported.
- Consider Alternative Browsers: Browsers like Firefox or Opera (older versions) can sometimes offer a more secure browsing experience.
- Virus Scan: Use a Virus Scan to verify the download.
13. The Hardware Factor: Is Your Card Simply Too Old?
Sometimes, the problem isn't software; it's the hardware itself.
- Outdated Standards: Older wireless cards might only support older WiFi standards (like 802.11b/g
1.3a - Koneksi internet dengan Windows XP

By jackjohn684 1.3a - Koneksi internet dengan Windows XP by jackjohn684
Bagaimana menghubungkan Windows XP ke jaringan nirkabel Anda
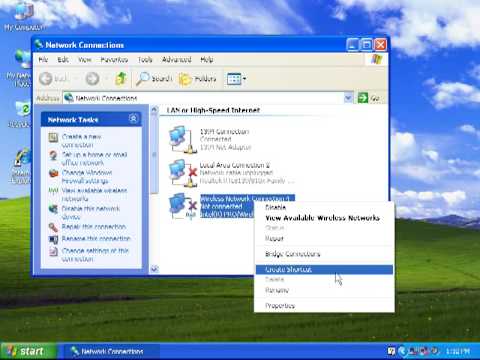
By NetComm Bagaimana menghubungkan Windows XP ke jaringan nirkabel Anda by NetComm

Title: Cara Memperbaiki Wifi Tidak Berfungsi di Windows XP Tutorial
Channel: MDTechVideos
Cara Memperbaiki Wifi Tidak Berfungsi di Windows XP Tutorial by MDTechVideos
Laptop Wifi Connect
Windows XP WiFi Connection: A Seamless Guide to Reconnecting
Navigating the digital landscape can feel daunting, particularly when confronted with technical hiccups. Among the most frustrating is the inability to connect to a Wi-Fi network, especially when using an operating system as enduring as Windows XP. While newer operating systems have streamlined the process, the legacy of Windows XP persists, and with it, the occasional challenge of establishing or re-establishing a wireless connection. This article serves as a comprehensive resource, providing a clear and precise guide to swiftly resolving WiFi connectivity issues on your Windows XP machine, ensuring you can get back online with minimal disruption.
Understanding the Connection Conundrum: Common Windows XP WiFi Roadblocks
Before diving into solutions, it’s vital to understand the potential culprits behind your Windows XP WiFi woes. Often, the problems stem from a few key areas: outdated or missing drivers, incorrect network settings, disabled wireless services, or, less frequently, hardware malfunctions. Pinpointing the source is the first step toward efficient troubleshooting.
1. Driver Dilemmas: Updating Your Wireless Network Adapter Drivers
One of the most frequent causes of WiFi connectivity issues is outdated or corrupted drivers for your wireless network adapter. Drivers are the software components that allow your operating system to communicate with the hardware. Outdated drivers can lead to compatibility problems, resulting in a failure to recognize or connect to available networks.
To address this, you must first determine the model of your wireless network adapter. This information is crucial for downloading the correct drivers. There are several ways to identify the adapter:
Device Manager. Right-click on "My Computer" (or "Computer") on your desktop or in the Start menu, and select "Manage". In the Computer Management window, click on "Device Manager" located in the left panel. Expand the "Network adapters" category. Your wireless network adapter will be listed here, and its name will provide you with the manufacturer and model.
Physical Inspection. If possible, check the physical hardware of your network adapter. On laptops, this is often a sticker or a marking on the underside of the device. For desktop computers with a separate wireless card, you might have to open the computer case.
Once you have the adapter's model, you can locate the latest drivers. Visit the manufacturer's website (e.g., Intel, Broadcom, TP-Link) and navigate to the "Support" or "Drivers" section. Search for your specific adapter model and download the most recent version.
After downloading the drivers, it's time to install them.
- Driver Installation. Usually, the download will be an executable file. Double-click on the file and follow any on-screen instructions to install the driver. Restart your computer once the installation is complete. After the reboot, try reconnecting to your wireless network.
2. Service Savvy: Verifying Wireless Services are Enabled
Windows XP relies on specific services to manage and maintain wireless connections. If these services are disabled or malfunctioning, your computer won’t be able to detect and connect to WiFi networks. You must check these services' status.
Accessing Services. Click on the "Start" button, then “Run.” In the Run dialog box, type
services.mscand press Enter. This action opens the Services window, where you can manage the services running on your system.Identifying Relevant Services. Look for the following two services:
- Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) or WLAN AutoConfig. This service manages wireless network connections, including the scanning for networks and the connection process.
- DHCP Client. This service is responsible for assigning an IP address to your network adapter, which is necessary for communication on the network.
Checking Service Status. Double-click each service to open its properties. Ensure that the "Startup type" for Wireless Zero Configuration is set to "Automatic" and that the "Service status" is "Started". If the service is not running, click the "Start" button. For DHCP Client, ensure "Startup type" is "Automatic" and the "Service status" is "Started". If it's not running, click the "Start" button. If you changed a setting, click "Apply."
Restarting Services. After verifying and, if necessary, starting the services, restart your computer. This reboot ensures that the changes have been properly implemented.
3. Network Settings Navigation: Configuring Your Wireless Connection
Incorrect network settings can often prevent a successful WiFi connection. Windows XP offers a straightforward interface for managing and configuring network connections.
Accessing Wireless Network Connection Settings. Double-click the wireless network icon located in your system tray (usually in the bottom-right corner of your screen). If you can’t find the icon, check in Control Panel under Network Connections.
Identifying and Troubleshooting the connection. Ensure that your wireless network is listed. If it is, sometimes a simple "Repair" of the connection can do the trick. Right-click on your wireless network connection and select "Repair." This action attempts to refresh the IP address and repair connectivity problems.
Understanding Encryption and Security Protocol. If you are prompted for a security key (also known as a WEP key or WPA/WPA2 password), ensure you are entering the correct key. This key is usually found on the router’s sticker or configured via the router’s web interface.
Advanced Settings. If you had no luck, you may need to dive into the advanced settings. Go to the properties of your wireless connection (Right-click and select "properties"), then under the "Networking" tab, ensure that the "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)" option is both selected and checked. If the TCP/IP settings are not set to "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS server address automatically," you may need to adjust these settings. In some cases, you may need to manually enter a static IP address and DNS server information, but only if your network administrator or the network itself requires this.
4. Hardware Hurdles: Investigating the Physical Connection
While less common, hardware issues can sometimes contribute to WiFi problems.
Physical Checks. Begin by checking the physical positioning of your wireless network adapter. Ensure that the adapter is properly seated in its slot (for desktop computers) or that the wireless switch is turned on (for laptops). If a switch is present, make sure the switch is enabled.
Router Reset. Restarting your router is a simple yet effective troubleshooting step. Unplug the router from the power outlet, wait for 30 seconds, and then plug it back in. Allow the router to boot up completely before attempting to reconnect to your WiFi network.
External Factors. Confirm that your physical environment isn't creating interference. Thick concrete walls, microwaves, and other electronic devices can sometimes interfere with the wireless signal. Consider moving your computer closer to the router or repositioning the router to improve signal strength.
Adapter Test. Try connecting a different device to the same WiFi network to determine if the problem is isolated to your Windows XP machine. If other devices can connect without issue, the problem likely lies within your computer's configuration or hardware.
5. Advanced Troubleshooting: Further Remedies
If the initial steps don't resolve the problem, you may need to delve into more advanced troubleshooting techniques.
System Restore. If the WiFi connection problem started recently, consider using System Restore. Select a restore point when your WiFi was working correctly. This action will revert your system to a previous state, potentially resolving driver conflicts or software incompatibilities.
Network Card Replacement. In rare cases, the wireless network adapter itself may be faulty. Consider replacing the network card if you've exhausted other troubleshooting steps and suspect a hardware failure.
Final Steps
Windows XP, while a veteran of the operating system world, paired with a careful approach to troubleshooting, remains a functional platform for getting online. By systematically working through the steps outlined in this guide – addressing driver problems, verifying service status, checking the connection settings, confirming the hardware status, and taking advanced troubleshooting steps – you should be able to restore or reconnect to your WiFi and get back to surfing the web. Embrace patience, persistence, and a clear understanding of the technical elements, and you’ll be back online quickly.

