laptop not connecting to wifi says plug in ethernet

Title: 7 Ways to Fix a Computer That Can't Find or Connect to Wifi Windows 10 Laptops & Desktops
Channel: Ask A Computer Geek
7 Ways to Fix a Computer That Can't Find or Connect to Wifi Windows 10 Laptops & Desktops by Ask A Computer Geek
Laptop Wifi Nightmare? Solved! (No Ethernet Needed!)
Banish Wi-Fi Woes: Your Laptop's Wireless Salvation (No Cables Required!)
Ever found yourself staring blankly at a flickering Wi-Fi icon, desperately wishing for a stable connection? It's a common frustration, isn't it? So many of us rely on laptops for work, entertainment, and staying connected. However, a glitchy wireless network can lead to endless problems. Therefore, let's delve into the depths of laptop Wi-Fi troubleshooting. Prepare yourself for an exciting journey.
The Phantom Problem: Diagnosing Your Wi-Fi Demons
First things first: let's figure out what's actually going on. Is it your laptop, or is the problem rooted elsewhere? Consequently, begin with the basics. Check other devices. Are your phone, tablet, or another laptop experiencing the same issues? If they are, the problem likely resides with your internet provider or router. On the other hand, if only your laptop is suffering, then it’s time to investigate further.
Check those Obvious Culprits
Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the most effective. Before launching into complex troubleshooting steps, double-check a few fundamental things. Is Wi-Fi switched on? Moreover, ensure your laptop's wireless adapter is enabled. Often, there's a physical switch on the side of your laptop, or a function key combination (like Fn + the Wi-Fi icon key) to toggle it. In addition, restart your laptop. This simple action can often resolve minor software glitches. Also, restart your router and modem. Often, they hold the key to restoring your internet connection.
Decoding Your Network: Signal Strength and Interference
Now, assess your signal strength. A weak signal often leads to dropped connections and slow speeds. Generally, you’ll see visual indicators in your system tray. Move closer to your router. Walls and other obstructions can weaken the signal. Additionally, be aware of potential interference. Other electronic devices, such as microwaves and cordless phones, can interfere. Try to move your router away from these sources. As a result, you can improve your Wi-Fi experience drastically.
Driver Drama: Updating and Troubleshooting Your Wireless Adapter
Your wireless adapter is the unsung hero of your Wi-Fi connection. Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause connectivity problems. Hence, you should consider updating your wireless adapter drivers. Head to your laptop manufacturer's website. Download the latest drivers for your specific model. You should install them. Alternatively, you can use Device Manager in Windows (or the equivalent on other operating systems). Right-click on your wireless adapter in the list. From there, you can update the driver automatically. Should that fail, try uninstalling and reinstalling the driver. This might also help.
Router Reset: A Fresh Start for Your Network
Sometimes, the problem isn't your laptop, but your router itself. Routers are complex devices. They need occasional resets. Begin by unplugging it from the power outlet. Wait for about 30 seconds. Then, plug it back in. This reboot can resolve various issues. If this doesn't work, consider resetting your router to its factory settings. Be warned, you'll need to reconfigure your Wi-Fi network details. This usually involves using a paperclip to press a tiny reset button on the router. Consult your router's manual for specific instructions.
Wireless Mysteries: Channel Selection and Bandwidth
Your router broadcasts on a specific channel. Overcrowded channels can cause interference. Therefore, access your router's settings. Then, change the Wi-Fi channel. Experiment with different channels (1, 6, and 11 are often recommended). Additionally, check your router’s bandwidth settings. Most modern routers support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 5 GHz band generally offers faster speeds, but it has a shorter range. However, the 2.4 GHz band provides better coverage. Experiment with each to see what works best for your environment.
The Ultimate Check: Hardware Considerations
Rarely, there may be a hardware issue. Your laptop's wireless adapter might be failing. If you tried all of the above steps and still can't connect, consider consulting a professional. A technician can diagnose and repair hardware problems. Similarly, a weak antenna could cause problems.
Final Thoughts: Reclaiming Your Wireless Freedom
Troubleshooting Wi-Fi problems can be a time-consuming process. However, with patience and the right approach, you can usually restore a stable connection. By systematically working through these steps, you can banish those frustrating Wi-Fi woes. You will maintain a smooth, uninterrupted connection. After all, a reliable wireless connection is vital for modern life. So, go forth, troubleshoot, and enjoy your newfound internet freedom!
Laptop WiFi Download Limit: SHOCKING Truth Revealed!Laptop Wifi Nightmare? Solved! (No Ethernet Needed!)
Hey everyone! Ever felt like your laptop is possessed by a wifi demon? One minute you're cruising the internet, the next – poof – connection lost. It's enough to make you hurl your laptop across the room. We've all been there. But fear not, weary travelers of the digital realm! We're diving deep into the abyss of wifi woes, surfacing with solutions that don't involve wrestling with ethernet cables (because let’s be honest, sometimes those are more trouble than they’re worth).
1. The Wifi Ghost in Your Machine: Recognizing the Problem
First things first, let’s diagnose the problem. Is it a phantom connection drop? A sluggish browsing experience that makes dial-up seem speedy? Or a complete "no internet" situation staring you in the face? Understanding the symptoms is key. Think of it like a doctor's visit; the more details you provide, the better the diagnosis. Are other devices in your home experiencing the same issues? This helps narrow down if it's your laptop or your entire network. We've experienced it all, from buffering videos that resemble a stuttering slideshow to downloads that crawl.
2. The Usual Suspects: Troubleshooting the Obvious (and Often Overlooked)
Before we launch into advanced strategies, let's tackle the easy fixes. These are the equivalent of checking if your car has gas before complaining about the engine.
- Restart Your Laptop: The classic. Turn it off, wait a minute, turn it back on. It's surprising how often this magic trick works.
- Restart Your Router and Modem: Unplug them both for a good 30 seconds. Think of it as a digital reset button.
- Check Physical Obstacles: Thick walls, metal objects, and even microwaves can interfere with your wifi signal. Try moving closer to the router or repositioning your laptop.
- Check Your Wifi Password: Seriously, we've all done it. Double-check you're entering the correct password.
3. Channel Surfing: Optimizing Your Router’s Wifi Channels
Alright, if the simple steps aren't cutting it, let’s get a little technical (but don't worry, we'll keep it simple). Routers broadcast on different channels. Imagine these channels like radio stations. Sometimes, your neighbors' networks are broadcasting on the same channel, causing interference and slowing things down.
- Access Your Router's Settings: You'll usually do this by typing your router's IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into your web browser.
- Find the Wifi Channel Settings: Look for a setting labeled "Channel," "Wireless Channel," or something similar.
- Experiment with Different Channels: Try channels 1, 6, and 11, as these are usually less congested. You might need to restart your router after changing the channel.
4. Upgrading Your Hardware: The Power of a Modern Router
Let’s face it, outdated hardware can be a bottleneck. If your router is older than your laptop, it might be time for an upgrade. Newer routers support the latest wifi standards (like 802.11ac or even the newer 802.11ax, also known as WiFi 6), which offer faster speeds and better range. Think of it like upgrading from a horse-drawn carriage to a sports car. The difference is noticeable!
5. Bandwidth Bonanza: Understanding the 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz Battle
Your router likely broadcasts on two different frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. What's the difference?
- 2.4 GHz: Offers better range, meaning it can reach further distances. But it's often slower and more prone to interference. Think of it as a sturdy, but not particularly fast, option.
- 5 GHz: Offers faster speeds and less interference, making it ideal for activities like streaming and gaming. However, it has a shorter range. Consider it the speed demon of wifi frequencies.
Try connecting to the 5 GHz network if it's available and you're close enough to the router. Otherwise, the 2.4 GHz might be your best bet for wider coverage.
6. Driver Dilemmas: Updating Your Wifi Adapter Drivers
Sometimes, the issue lies within your laptop itself, specifically your wifi adapter’s drivers. These are software programs that allow your computer to communicate with the wifi hardware. Outdated drivers can cause all sorts of problems.
- Open Device Manager: Search for "Device Manager" in the Windows search bar.
- Expand "Network Adapters": Locate your wireless network adapter (it might be called something like "Wi-Fi Adapter" or "Wireless Network Adapter").
- Right-Click and Update Driver: Select "Update driver" and follow the prompts. Windows will usually search for and install the latest driver automatically.
- Consider A Clean Installation: If updating does not work, it may also be necessary to remove the adapter from the system, restart the computer and reinstall the driver.
7. The Hidden Culprit: Interference From Other Devices
Your wifi signal can be easily disrupted. Microwaves, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, and even some wireless phones can all emit radio waves that interfere with your wifi signal.
- Identify Potential Culprits: Consider what devices are near your router and laptop.
- Experiment with Placement: Try moving your router or laptop away from these devices to see if it improves the connection.
- Consider Using Bluetooth Devices Less or Disabling Them: If you can, temporarily disable Bluetooth devices to see if it improves things.
8. Security Settings: WPA2 vs. WPA3 (And Why It Matters)
Your security settings aren't just about keeping your data safe; they can also affect your wifi performance. WPA2 is a common security protocol, but WPA3 is newer and offers improved performance and security.
- Access Your Router's Settings: You'll need to log in to your router's settings, as described earlier.
- Find the Wireless Security Settings: Look for a setting that says "Security," "Wireless Security," or something similar.
- Check Your Security Protocol: See if your router supports WPA3. If so, try enabling it. (Note: Some older devices may not work with WPA3).
9. The Wireless Network Troubleshooter: Let Windows Be Your Guide
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter that can often identify and fix common wifi problems.
- Right-Click the Wifi Icon: Click on the wifi icon in the system tray (usually in the bottom right corner of your screen).
- Select "Troubleshoot Problems": Windows will then attempt to automatically diagnose and fix any issues. This is like calling a help desk for your laptop.
10. The Powerline Adapter: Extending Your Network's Reach
If your wifi range is the issue, and you don't want to run ethernet cables, consider a powerline adapter. These devices use your home's electrical wiring to extend your network.
- Plug One Adapter Near Your Router: Connect it to an electrical outlet and plug an ethernet cable from your router into the adapter.
- Plug Another Adapter Near Your Laptop: Connect it to an electrical outlet and plug an ethernet cable from your laptop into the adapter.
- Consider This Solution a Wifi Amplifier: This effectively creates a wired connection without the need for long ethernet cables.
11. The Wifi Extender: Boosting Your Wifi Signal
A wifi extender (also sometimes called a repeater) takes your existing wifi signal and rebroadcasts it, extending its reach.
- Placement is Key: Place the extender in a location that's within range of your router and where you want to extend the wifi coverage.
- Setup is Usually Straightforward: Extenders are typically easy to set up, often with a simple setup wizard.
- Note That Extenders Can Reduce Speed: Extenders can sometimes reduce your overall wifi speed, so consider this before fully committing to this solution. It's like a middle man, slightly slowing down the process.
12. DNS Diving: Changing Your DNS Server
Your Domain Name System (DNS) server translates website addresses (like google.com) into IP addresses that your computer can understand. Sometimes, your default DNS server can be slow or unreliable.
- Change Your DNS Settings: You can manually change your DNS server settings in your network connection properties. Use a service like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
13. MAC Address Filtering: Adding an Extra Layer of Security
MAC address filtering allows you to specify which devices are allowed to connect to your network. This adds an extra layer of security and can sometimes help prevent unexpected connection issues.
- Find Your Laptop's MAC Address: You can find this in your network adapter settings.
- Access Your Router's Settings: Log in to your router's settings.
- Enable MAC Address Filtering: Add your laptop's MAC address to the list of allowed devices
Network cable unplugged error in Windows 10 11 Fix
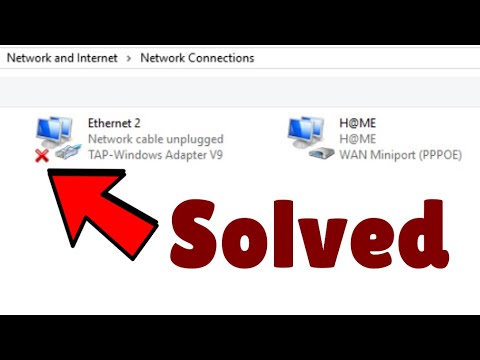
By The Geek Page Network cable unplugged error in Windows 10 11 Fix by The Geek Page
Fix Network Cable Unplugged Error In Windows 11 & 10 - Full Guide

By GuideRealm Fix Network Cable Unplugged Error In Windows 11 & 10 - Full Guide by GuideRealm
If your PC won't connect to the internet shorts pctips tech

By RTC Tutorials If your PC won't connect to the internet shorts pctips tech by RTC Tutorials

Title: Fix A Network Cable Is Not Properly Plugged In Or May Be Broken Windows 10
Channel: ComeAndFixIT
Fix A Network Cable Is Not Properly Plugged In Or May Be Broken Windows 10 by ComeAndFixIT
Laptop Wifi Hotspot
Laptop Wi-Fi Nightmare? Solved! (No Ethernet Needed!)
Have you ever stared, exasperated, at your laptop screen, the dreaded Wi-Fi symbol mocking your attempts to connect? The spinning wheel of doom. The frustrating "no internet" error message. We’ve all been there. Whether you're a seasoned digital nomad, a student cramming for an exam, or simply trying to unwind with your favorite streaming service, a reliable Wi-Fi connection is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. But what happens when your Wi-Fi consistently fails you? What if you’re tethered to a desk because you believe you need an Ethernet cable, sacrificing the very portability your laptop promises? Fear not, because we will break down the common culprits behind Wi-Fi woes and provide you with practical, effective solutions – no Ethernet cable required.
Decoding the Wi-Fi Wasteland: Unveiling Common Connectivity Culprits
Before launching into solutions, let's identify the usual suspects. Understanding the root cause of your Wi-Fi issues is the first step toward a permanent fix.
- The Router's Rebellion: Your router, the central hub of your home or office network, is the most common point of failure. It could be overloaded, outdated, or simply experiencing a temporary glitch. Over time, routers, burdened with too many connected devices, can become sluggish or unresponsive. Firmware updates, essential for security and performance, might have been neglected. Physical obstructions (walls, metal objects) can severely impede its signal.
- Device-Specific Dilemmas: Your laptop itself can be the problem. The Wi-Fi adapter, the built-in hardware responsible for connecting to wireless networks, can have driver issues, leading to inconsistent connectivity. Software conflicts, interfering background processes, or outdated operating systems can all contribute to connection failures. Even physical damage to the adapter or antenna can be the culprit.
- Network Neighborhood Troubles: The surrounding environment plays a role. Competing Wi-Fi signals from your neighbors can cause interference, especially on the 2.4 GHz band, which is more prone to congestion. This "Wi-Fi pollution" can lead to dropped connections, slow speeds, and general instability.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP) Impasses: Sometimes, the issue isn’t with your equipment at all; it’s with your internet service provider. Outages, scheduled maintenance, or bandwidth bottlenecks can temporarily disrupt your internet connection. While less frequent, these issues can disrupt your Wi-Fi and online experience.
Troubleshooting Techniques: Restoring Your Wireless Harmony
Now, let’s dive into the practical solutions. We'll start with the simplest steps and progress to more advanced troubleshooting, all without needing an Ethernet cable.
1. The Reboot Routine (and Why It Matters):
This might seem too simple, but a reboot often works.
- Router Reboot: Unplug your router from its power source. Wait a full 60 seconds (yes, a full minute). This allows the router's capacitors to fully discharge and reset its internal processes. Plug it back in and wait for the router to fully power up and reconnect to your ISP (usually indicated by a solid or flashing internet light). Test your connection.
- Laptop Reboot: Restart your laptop. This clears temporary files, resets software, and often resolves minor glitches that might be interfering with your Wi-Fi connection.
2. Driver Detective Work: Ensuring Your Wi-Fi Adapter is Up-to-Date:
Outdated or corrupted drivers are a frequent source of Wi-Fi woes. Updating your Wi-Fi adapter driver can frequently remedy the problem.
- Windows: Press the Windows key + X, and select "Device Manager." Expand the "Network Adapters" section. Right-click on your Wi-Fi adapter (it will be named something like "Intel Wireless-AC 9260" or "Realtek 8821CE Wireless LAN 802.11ac PCI-E NIC") and select "Update driver." Choose to "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will search for and install the latest drivers. If that doesn't work, you can try uninstalling the driver and restarting your laptop, which often prompts Windows to reinstall the driver automatically.
- macOS: Click the Apple menu, then "System Preferences," and then "Software Update." macOS usually keeps your drivers updated automatically, but it never hurts to check. If there are any updates available, install them.
3. Location, Location, Location: Optimizing Router Placement:
Where you place your router significantly impacts your Wi-Fi signal strength and range.
- Central Positioning: Place your router in a central location within your home or office to ensure the signal reaches all your devices effectively.
- Elevation Matters: Place your router on a shelf, desk, or table, elevated off the floor. This allows the signal to radiate outward and upward, avoiding obstacles.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Keep your router away from walls, metal objects, mirrors, and appliances that can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal. Microwaves, in particular, are notorious signal blockers.
- Antenna Adjustment: If your router has external antennas, experiment with different orientations. Try positioning them vertically, horizontally, or at various angles to find the optimal signal strength for your specific environment.
4. Channel Surfing: Finding the Least Congested Wi-Fi Highway:
Wi-Fi routers broadcast signals on different channels within the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. Choosing a less crowded channel can dramatically improve your connection speed and stability.
- The 2.4 GHz Band: This band offers broader coverage but is more prone to interference. Use a Wi-Fi analyzer app on your smartphone (like Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android or Airport Utility for iOS) to scan for nearby Wi-Fi networks. Identify the channels with the least activity and configure your router to use one of those channels. Access your router's configuration page (usually by typing its IP address, like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1, into your web browser) and navigate to the "Wireless" or "Wi-Fi" settings to change the channel.
- The 5 GHz Band: This band offers faster speeds and less interference than the 2.4 GHz band, but it has a shorter range. If your laptop and router support 5 GHz, and you don't need extensive coverage, switch to this band for a superior experience.
5. Software Savvy: Minimizing Interference on Your Laptop:
Unwanted software can sometimes interfere with Wi-Fi connectivity.
- Close Unnecessary Applications: Close any applications consuming significant resources, especially those that use the internet heavily.
- Disable VPN Software (Temporarily): If you use a VPN, temporarily disable it to see if it's causing connection problems. Some VPN services can interfere with Wi-Fi.
- Run a Malware Scan: Malware can sometimes disrupt your network connection. Run a full system scan with your antivirus software to eliminate any potential threats.
6. DNS Diagnostic: Improving Internet Communication:
DNS (Domain Name System) servers translate website addresses into IP addresses. Sometimes, your ISP's DNS servers can be slow or unreliable. Changing to a public DNS server might improve browsing speed and connection stability.
- Google Public DNS: In your operating system's network settings, change the DNS servers to Google's public DNS servers: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4.
- Cloudflare: You can also use Cloudflare's DNS servers: 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1.
7. Signal Boosting: Extending Your Wi-Fi Reach (Without Ethernet)
If your Wi-Fi signal struggles to reach certain areas of your home or office, consider these solutions:
- Wi-Fi Extenders/Repeaters: These devices rebroadcast your existing Wi-Fi signal, extending its range. Place them halfway between your router and the area where the signal is weak.
- Mesh Wi-Fi Systems: These systems use multiple nodes throughout your home to create a single, seamless Wi-Fi network. This solution is ideal for larger homes or environments with multiple obstructions.
8. Resetting Network Settings (A Last Resort):
If all else fails, resetting your network settings can sometimes resolve stubborn Wi-Fi problems, especially if you suspect misconfigurations or software conflicts.
- Windows: Go to "Settings" -> "Network & Internet" -> "Network reset." This will revert your network adapters to their default settings.
- macOS: Open "System Settings" -> "Network." Click the three dots next to your connected Wi-Fi network and choose "Remove." Then, reconnect to your Wi-Fi network. If this fails, you could try resetting your network settings to default, but be aware that this will drop all your network settings. Consult Apple's support website for instructions on how to do this, or contact their support staff for aid.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Wi-Fi Optimization Techniques
For the tech-savvy user, here are a few advanced techniques you could consider.
Advanced Router Configuration:
- Firmware Updates: Regularly update your router's firmware. These updates often include performance improvements, security patches, and bug fixes.
- Quality of Service (QoS): QoS allows you to prioritize certain types of network traffic,
