how to share wifi connection from laptop windows 7

Title: How to Create a WiFi Hotspot with Windows 7
Channel: 1stepatatime
How to Create a WiFi Hotspot with Windows 7 by 1stepatatime
Unlock Your WiFi: Share Your Laptop's Connection (Windows 7 Trick!)
Share Your Internet: A Windows 7 Secret Revealed!
Ever wished you could share that precious internet connection from your laptop? We've all been there. Maybe your router failed, or you're stuck in a hotel room. The good news? Windows 7 offers a hidden trick. You can transform your laptop into a Wi-Fi hotspot. So, let's explore this surprisingly simple process.
The Magic of Hosted Networks: What Are They?
Before diving in, let's grasp the concept. A hosted network is a software-created virtual Wi-Fi adapter. It allows your existing Wi-Fi adapter to act as a transmitter. In essence, it creates a second virtual network interface. Thus, your laptop broadcasts its internet connection. This is remarkably beneficial. You can share your internet with other devices. These include smartphones, tablets, and other laptops.
Setting the Stage: Preparation is Key
Before we start, ensure a few things. Firstly, make sure your laptop has a working Wi-Fi adapter. Secondly, you need a stable internet connection on your laptop. This could be from an Ethernet cable or an existing Wi-Fi network. Thirdly, you need administrator privileges. We'll be working with system-level settings here. The process is relatively straightforward. However, proper preparation makes it smoother.
Step-by-Step: Creating Your Virtual Hotspot
Alright, let's get technical! Don't fret, though. We’ll guide you.
First, open the Command Prompt. You can do this by typing "cmd" in the Start menu search. Then, right-click "Command Prompt". Select "Run as administrator". This is crucial for the process to function.
Next, we initiate the hosted network. Therefore, type the following command and press Enter: netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid=YourNetworkName key=YourPassword. Replace "YourNetworkName" with your desired network name. Then, set "YourPassword" to a secure password. This password protects your network. Moreover, this helps keep unwanted users out.
After that, we configure internet connection sharing. Go to “Network and Sharing Center”. Find this in the Control Panel. Then, click "Change adapter settings". Here, identify the adapter with your internet connection. It could be Ethernet or Wi-Fi. Right-click the appropriate adapter. Choose "Properties".
Following this, navigate to the "Sharing" tab. Check these details carefully. You'll see a box labeled "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection." Check this box. From the dropdown menu, select your newly created hosted network. Its name matches your setup. Finally, click "OK".
Activating the Hotspot: Bringing It to Life
Now that the groundwork is complete, it's time to activate the hotspot. Return to the Command Prompt. Ensure it's still running as an administrator. Type the following command: netsh wlan start hostednetwork. Press Enter. You should see a confirmation message. Your hotspot is active.
Troubleshooting: Common Roadblocks and Solutions
Things don't always go smoothly. Therefore, let's address some common issues.
If the hosted network fails to start, check your network adapter drivers. Outdated drivers can be a culprit. Update them. Also, double-check the SSID and password. Ensure they're correct. Furthermore, verify the network adapter's mode. Make sure it's set to "allow" in the netsh command.
Still facing trouble? Confirm that other network-related services are running. Ensure the "WLAN AutoConfig" service is running. Furthermore, check the "Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)" service. You can find these in the Services app. Search for it in the Start menu.
Securing Your Network: Essential Considerations
Security comes first. Use a strong password for your Wi-Fi network. Change it regularly. Also, only share your connection with trusted devices. Enable a firewall on your laptop. This adds an extra layer of protection. Consider using a VPN. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic. Thus, it provides additional security.
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Freedom of Sharing
Sharing your internet connection is incredibly useful. Windows 7 offers a simple yet powerful solution. By following these steps, you can create a Wi-Fi hotspot. Thus, connect multiple devices. You've acquired a valuable skill. You can now spread internet access. So, go ahead, share the connection!
Laptop Won't Connect to WiFi? This ONE Weird Trick Fixes It!Unlock Your WiFi: Share Your Laptop's Connection (Windows 7 Trick!)
Hey there, fellow tech explorers! Remember those days when internet access was a precious commodity, like a golden ticket? We've come a long way, haven't we? Today, we're going to dust off an old, trusty trick – sharing your laptop's Wi-Fi connection. And, yes, this is specifically for those Windows 7 veterans still rocking it (or, maybe, inheriting it). Think of it as a secret handshake to unlock a world of shared internet bliss!
1. The Wi-Fi Wilderness: Why Share Your Connection?
Before we dive in, let's paint a picture. Imagine a scenario: you're in a hotel room, Grandma's basement, or a friend's place that's mysteriously Wi-Fi-less. You have internet access on your laptop, but your tablet, phone, or that vintage Nintendo DS of yours, is left stranded in the digital desert. This is where our Windows 7 wizardry comes in handy. Sharing your connection turns your laptop into a personal Wi-Fi hotspot, a lighthouse in a sea of connectivity woes!
2. Windows 7's Hidden Gem: The Ad-Hoc Network
Alright, time to roll up our sleeves. Windows 7, in its wisdom, buried a feature called an "Ad-Hoc Network." Think of it as a secret society for devices. It allows your laptop to broadcast its internet connection to nearby devices. It's not the most modern solution, but it's a reliable workhorse, like that favorite, well-worn pair of jeans that always fit.
3. Before We Begin: A Few Heads-Up
- Internet Connection: You, of course, need an active internet connection on your laptop. No internet, no sharing. Simple as that!
- Network Adapter: Make sure your laptop has a wireless network adapter. This is the antenna that does all the magic.
- Security First: We'll be creating a password for your Wi-Fi hotspot. Safety is paramount! Think of it as locking your digital front door.
4. Step-by-Step: Creating Your Ad-Hoc Network – Operation: Access Granted!
Let's get our hands dirty! This is where the fun begins.
- Open the Network and Sharing Center: Navigate to your Control Panel. You can often find it by clicking the Windows Start button and typing "Control Panel" in the search bar.
- Go to "Set up a new connection or network": In the Network and Sharing Center, you'll see a menu. Click on this option.
- Choose "Set up a wireless ad hoc (computer-to-computer) network": This is the key! Select this option. It might feel a bit old-school, but it's the gateway to sharing your connection.
- Network Name and Security: Give your new network a name. Something memorable is always good (like "Grandma'sInternet," or whatever your heart desires). Choose "WPA2-Personal" as your security type. This is the most secure option. Set a strong password. Don't make it "password"!
- Share Your Connection: When asked to "Turn on internet connection sharing?", choose "Yes." This is the green light to start sharing!
5. Fine-Tuning Your Connection: The Optional Tweaks
Now that we’ve created our ad-hoc network, there are just a couple of small tweaks and adjustments before we are off to the races.
- Allow Other Network Users to Connect Through This Computer’s Internet Connection: This is vital to make sure the internet connection will get shared properly. Navigate to: Control Panel -> Network And Internet -> Network and Sharing Center -> Change adapter setting. Right-click on the network connection you use to connect to the internet and choose "Properties." Now, navigate to the "Sharing" tab and check the box of "Allow other network users to connect through the computer’s internet connection."
- IP Addressing (If Needed): Sometimes, devices can struggle to get an IP address via the Ad-Hoc network. Here’s how to fix it. Navigate to: Control Panel -> Network And Internet -> Network and Sharing Center -> Change adapter setting. Right-click on the network connection your Ad-Hoc network uses and choose "Properties." Now, choose "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and choose "Properties." Be sure that you are getting the IP address automatically.
6. Connecting Your Other Devices: The Digital Party!
Alright, the party's about to start! Grab your other devices – phone, tablet, or whatever needs Wi-Fi.
- Scan for Networks: On the device you want to connect, go to your Wi-Fi settings. Scan for available networks.
- Find Your Network: You should see the network name you created in Step 4. Tap on it.
- Enter the Password: Enter the password you created. Boom! You should be connected.
7. Troubleshooting Troubles: When Things Go Sideways
Ah, the inevitable hiccup! Let's tackle some common issues.
- Devices Can't Find the Network: Double-check that your laptop's Wi-Fi is enabled and that you’ve followed the steps correctly.
- Can Connect, But No Internet: Ensure your laptop has an active internet connection. Also, double-check the "Sharing" settings mentioned in Section 5.
- Slow Speeds: Ad-Hoc networks aren't the fastest. If speeds are atrocious, consider other options if possible.
8. Ad-Hoc Network Limitations: Playing Fair
Let's be honest, Ad-Hoc networks are not perfect.
- Limited Range: The signal range is usually shorter than a regular Wi-Fi router. Think of it as a small, localized party.
- Security: Using WPA2-Personal is good, but it's not the same level of security as modern routers. Use this with caution.
- Compatibility: Some devices might struggle to connect.
9. The Modern Alternatives: Beyond Windows 7
While this is about Windows 7, let's acknowledge the elephant in the room. Modern operating systems (Windows 10/11, macOS, etc.) have evolved.
- Mobile Hotspot Feature: Most have a built-in mobile hotspot feature, usually easier to set up and more secure.
- Wi-Fi Router Options: Consider a portable Wi-Fi router if sharing is a frequent need.
10. When To Use This Trick: Situational Awareness
When is this trick useful?
- Emergency Situations: When no other internet is available.
- Sharing with a Few Devices: Like a small, intimate gathering.
- Temporary Solutions: When you need a quick fix, this is golden.
11. Safety First: Security Dos and Don'ts
- Strong Passwords: Always use a strong password.
- Trustworthy Devices: Only connect devices you trust.
- Turn Off When Done: Turn off the hotspot when you’re finished sharing.
12. The Speed Factor: Expectations vs. Reality
Don’t expect lightning-fast speeds. Be mindful of what you're doing. Streaming heavy content might not be ideal.
13. Windows 7 Lifeline: Staying Connected on Legacy OS
This trick is a lifesaver for those still using Windows 7. It keeps them connected when modern alternatives aren't available.
14. Beyond the Basics: Advanced Tweaks
For tech-savvy users, there are more advanced settings to explore. You can check the IP address of any client, and you can control who connects.
15. Embracing the Tech-Savvy Spirit: Keep Exploring
The digital world is constantly changing. Keep learning, experimenting, and solving problems. That’s the spirit of a true tech explorer!
Conclusion: The Wi-Fi Whisperer’s Guide
Alright! We've armed ourselves with the knowledge to share our laptop's Wi-Fi connection using a Windows 7 trick. This isn't just about sharing internet; it's about empowering ourselves with knowledge, adapting to the digital landscape, and helping others in the process. We've taken a leap back in time, revisiting older methods, all while keeping our digital toolkit honed. So, the next time you find yourself in a Wi-Fi wilderness, remember this guide and become the Wi-Fi whisperer you were always meant to be! Now go forth and share the connection!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is this safe to use?
Yes, if you use a strong password and only connect trusted devices. It's always good to be cautious in the digital world.
2. Why isn’t my device connecting?
Double-check the password, network name, and make sure your laptop's Wi-Fi is on. Also, ensure you have an active internet connection.
3. Can I connect multiple devices?
Yes, within the limitations of the Ad-Hoc network's signal range and bandwidth.
4. Is this faster than a regular Wi-Fi router?
Often, no. Ad-Hoc networks are not as fast
**Laptop WiFi Speed? CMD's Secret Weapon! (Shockingly Fast)**How to Share WiFi From Laptop - Windows 7810

By GizPrime How to Share WiFi From Laptop - Windows 7810 by GizPrime
Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011

By inprez id Cara Download & Install Driver WIFI & ETHERNET Manual untuk Windows 781011 by inprez id
How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
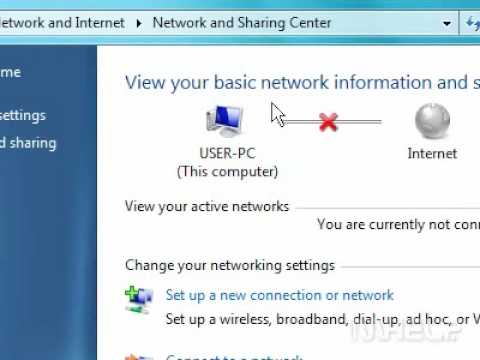
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U

Title: Cara Mengaktifkan Hotspot Wifi Laptop Windows 7
Channel: LAPTOP TUTORIAL
Cara Mengaktifkan Hotspot Wifi Laptop Windows 7 by LAPTOP TUTORIAL
Working With Laptop
Unlock Your WiFi: Share Your Laptop's Connection (Windows 7 Trick!)
Navigating the digital landscape requires a reliable internet connection, and sometimes, fate, or simply a lack of available WiFi, leaves you in a bind. Perhaps your phone is running low on data, a friend needs connectivity, or that vital presentation needs to be uploaded immediately. Whatever the scenario, transforming your Windows 7 laptop into a WiFi hotspot is a powerful, yet often overlooked, skill. This guide unveils the secrets to sharing your laptop's existing internet connection, turning it into a wireless access point that can accommodate multiple devices.
Understanding the Infrastructure: Why Share Your Connection?
Before diving into the how-to, it's crucial to understand the benefits of sharing your laptop's internet. Firstly, it provides an immediate solution for devices lacking direct access to a WiFi network. This is particularly useful in hotels, coffee shops with unreliable WiFi, or areas with limited network coverage. Secondly, it can serve as a backup solution when your primary internet source fails, allowing you to use your laptop's tethered smartphone connection or a wired Ethernet link to create a temporary WiFi hub. Thirdly, it’s a cost-effective measure. Instead of purchasing a separate mobile hotspot device, you can leverage the hardware you already own, your Windows 7 laptop, to provide internet access. This versatility ensures a continuous flow of connectivity, regardless of circumstances.
The Foundation of Sharing: Checking Your Laptop's Capabilities
Before you begin, it's vital to ensure your laptop is compatible with the necessary features. Windows 7, while a legacy operating system, provides the fundamental tools needed to create a WiFi hotspot. However, the critical component is your laptop's wireless network adapter. Most modern laptops include a wireless card capable of acting as a wireless access point. To verify this, access your Windows 7 Device Manager. To achieve this, navigate the Start Menu, open the Control Panel, select System and Security, then choose Device Manager. Expand the Network adapters section. Identify your wireless network adapter, typically labeled with terms like “Wireless Network Adapter” or “WiFi Adapter.”
If your adapter is present and functions correctly, you're in good shape. If it's missing or displays an error, you may need to update the driver. You can usually download the latest drivers from your laptop manufacturer's website. Furthermore, ensure your laptop has a stable internet connection. This can be through an Ethernet cable or an existing WiFi network. Without a functional internet connection, you won't be able to share anything.
Method 1: Using the Command Prompt (The Power User’s Approach)
This method provides a more hands-on, in-depth approach to creating a WiFi hotspot via the command line. It offers greater control over your hotspot's settings.
Step 1: Launching the Command Prompt:
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. To do this, find "cmd" in the Start Menu search bar, right-click on it, and select "Run as administrator."
Step 2: Setting Up the Hosted Network:
Type the following command and press Enter:
netsh wlan set hostednetwork mode=allow ssid="YourHotspotName" key="YourPassword"
Replace "YourHotspotName" with the desired name for your WiFi hotspot. Choose a strong and unique password for "YourPassword". This step allows the operating system to set up the core elements of the hotspot.
Step 3: Starting the Hosted Network:
After setting up the network, initiate the hotspot by entering this command, and subsequently pressing Enter:
netsh wlan start hostednetwork
If successful, this command activates the WiFi hotspot. You should see a confirmation message.
Step 4: Sharing the Internet Connection:
The final step involves sharing your existing internet connection. This is crucial for enabling other devices to actually access the internet through your new hotspot. Follow these steps exactly:
- Open the Network and Sharing Center through the Control Panel.
- Click on "Change adapter settings" on the left-hand side. This brings up the Network Connections window.
- Identify the adapter that's used for your active internet connection (e.g., your Ethernet adapter or the WiFi adapter you're currently connected to the internet with).
- Right-click on this adapter and select "Properties".
- Go to the Sharing tab.
- Check the box that says "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection".
- In the drop-down menu under "Home networking connection," select Microsoft Hosted Network Virtual Adapter. This is the virtual adapter created by the previous steps.
- Click "OK" to save settings.
At this point, your WiFi hotspot should be active and readily available for other devices to connect to.
Method 2: Using Virtual Router Manager (GUI for Simplicity)
For those who prefer a graphical user interface (GUI), a third-party application is available. Virtual Router Manager simplifies the process.
Step 1: Downloading and Installation:
Download Virtual Router Manager from a reputable source. The program is generally lightweight and straightforward to install.
Step 2: Configuration:
Launch Virtual Router Manager. You'll be prompted to set your network name (SSID) and password. Configure these settings carefully. Under "Shared Connection," select the active internet connection, allowing the software to share it with other devices.
Step 3: Starting the Hotspot:
Click "Start Virtual Router" to activate the hotspot. The program will then manage the hotspot, simplifying the necessary configurations.
Troubleshooting Common Hurdles
While the process is usually seamless, a few potential setbacks can occur. We'll delve into the common issues and solutions.
1. Hosted Network Not Supported:
If you encounter errors suggesting that the hosted network is not supported, ensure your wireless network adapter driver is up to date. Outdated drivers can cause compatibility problems. Also, verify that your wireless adapter is indeed capable of acting as an access point.
2. Internet Connection Sharing Issues:
Sometimes, the internet connection sharing won't properly work. Double-check the steps outlined earlier. Verify that the "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection" box is checked and that you’ve selected the correct home networking connection. Restarting the computer and the router may also resolve this issue.
3. Connectivity Problems:
If devices are connecting to your hotspot but not accessing the internet, it is because of network settings. Ensure that your computer's firewall isn't blocking the connection. Also, verify that you’ve chosen the correct internet connection to share.
4. Slow Speeds:
Sharing your internet connection invariably reduces available bandwidth. The more devices connected, the slower the experience. Consider upgrading your existing internet package if experiencing persistent slowdowns.
Optimizing Your Experience: Best Practices
For a smoother experience, consider the following best practices:
- Choose a Strong Password: Protect your hotspot from unauthorized access by creating a robust, unique password.
- Monitor Connected Devices: Keep track of devices connected to your hotspot to prevent overuse and conserve bandwidth.
- Name Your Hotspot Appropriately: Select a clear and descriptive name for your hotspot to make it easily identifiable.
- Regularly Update Drivers: Ensure your wireless network adapter drivers are always up to date.
- Familiarize Yourself with Network Settings: Learn about your computer's firewall settings and other related configurations.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Tweaks
Seasoned users might explore advanced customizations. You can modify the channel your hosted network uses to minimize interference from other WiFi networks. This can be done within the Command Prompt using the netsh wlan set hostednetwork channel=X command, replacing "X" with the desired channel number (usually between 1 and 11). However, these settings may only be effective if the devices support it.
Ensuring a Secure Connection
Security is paramount. Using WPA2-Personal encryption, which is standard, is a solid starting point, protecting your data. Avoid using older encryption protocols such as WEP, as they are notoriously vulnerable. Also, regularly change your password and, if possible, enable MAC address filtering within the hotspot's settings to limit access to only authorized devices.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Connectivity
Creating a WiFi hotspot on your Windows 7 laptop is a powerful trick that expands your connectivity options. By utilizing this guide, you have the knowledge to share your internet connection with ease. Whether you’re traveling, helping a friend, or just need a quick fix, your laptop can become a valuable asset. Embrace the power of shared connectivity and explore the possibilities that come with it. You now have the tools to stay connected, wherever you are.
