how to connect laptop to pc via wifi windows 7
Title: How to transfer files from PC to PC using WiFi Windows 10 7 8
Channel: IT Magics
How to transfer files from PC to PC using WiFi Windows 10 7 8 by IT Magics
Laptop to PC WiFi: Windows 7 Secret Trick Revealed!
Unlocking Wireless Wonders: Seamlessly Connecting Your Laptop to Your PC via WiFi (Even with Windows 7!)
Ever wished you could effortlessly share files, access your PC's internet connection, or even play multiplayer games with your laptop and PC chatting? You're in for a treat, because we are about to reveal a fantastic secret trick that has helped many users in the past. Setting up a wireless connection between your laptop and PC is easier than you might believe. Fortunately, this guide covers a method that many utilize, and it's especially rewarding when using Windows 7!
The Hidden Gateway: Ad-Hoc Networks – Your Secret Weapon
So, what's the secret? It’s the often-overlooked ad-hoc network. In fact, it's a simple, peer-to-peer wireless network, created without a central router. It allows two or more devices to connect directly to each other. Initially, setting it up might sound very complex. However, trust me, it's a straightforward process, particularly when you use Windows 7. You should know that the concept is beautiful in its simplicity, allowing for a direct link between your devices.
Step-by-Step Setup: We’re Making it Easy!
Let's dive in. First, ensure both your laptop and PC have Wi-Fi capabilities. Then, follow these easy steps:
Initiate the Connection on Your PC:
- Begin with your PC. Open the "Network and Sharing Center" via the Control Panel. You have to navigate there. You can do so by searching for it in the Start menu.
- Click on "Set up a new connection or network." That's the crucial first step.
- Choose "Set up a wireless ad-hoc (computer-to-computer) network" and click "Next."
Customize Your Wireless Network:
- Give your network a distinctive name. This will help you identify it later. Now, you must also choose a security type. WPA2-Personal is generally recommended for improved security. So, utilize that.
- Enter and confirm a strong password. Remember this password! You'll need it for both devices. Importantly, this safeguards your connection.
- Check the box that says "Save this network." Ultimately, it helps you. Click "Next." It will configure the network settings.
Connect Your Laptop:
- Turn on your laptop’s Wi-Fi.
- Search for available networks. You should spot the ad-hoc network you just created on your PC.
- Select your network.
- Enter the password when prompted.
- Click "Connect".
Fine-Tune Network Settings (Important!):
On your PC, go back to "Network and Sharing Center." Click "Change adapter settings."
Right-click on your wireless network adapter. Select "Properties." You must select this.
Find "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" in the list.
Click on "Properties." At this step, the configuration is essential.
Select "Use the following IP address:"
- IP address: 192.168.1.1
- Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
Click "OK" on both windows. Then, click "Close".
On your laptop, follow the same steps as above. Then, configure your laptop's IP address. You must use:
- IP address: 192.168.1.2
- Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
Click "OK" on both windows. At that point, it should be ready.
Sharing and Accessing Resources: Making it Efficient
Now that your devices are connected, the real fun begins! You will need to know how to share your resources.
Enable File Sharing: On your PC, locate the files or folders you wish to share. Right-click them, and choose "Share." Then, select "Specific people." Choose "Everyone" in the dropdown menu and add it. Set the permission level to "Read/Write" if you want to modify files from your laptop. Make certain this is what you desire. Click "Share."
Access Files from Your Laptop: Open File Explorer on your laptop. In the left-hand navigation pane, click on "Network." You should see your PC. Click on the PC’s icon. You'll be asked for credentials. Then, enter your PC’s username and password if prompted. Now, you can access shared folders and files. And you can also copy them to your device.
Troubleshooting Tips: Dealing with Potential Roadblocks
Occasionally, you might encounter some minor hiccups. However, don't worry! Here are some solutions.
Connectivity problems: Double-check the network name and password. Ensure you entered them correctly on both devices. Also, make sure your firewall isn’t blocking the connection. You should temporarily disable your firewall to test this. Then, re-enable it afterward.
File sharing issues: Ensure the folders are actually shared. Verify that the permissions are properly set to allow access from your laptop. Furthermore, consider restarting both your PC and laptop.
Internet Access: If you are trying to access the Internet from your laptop through the PC, ensure your PC is connected to the internet. The PC must have an active internet connection. Finally, enable "Internet Connection Sharing" on your PC.
Beyond Windows 7: General Applicability
While this guide focuses on Windows 7, the principles are somewhat similar for other operating systems. The core concepts of ad-hoc networks remain consistent. However, the exact steps might slightly vary depending on your OS. It will involve checking the settings. So, adjust the procedure for your Windows 10, Windows 11, or even macOS.
Reaping the Rewards: Unleashing the Power
With this method, you've unlocked a versatile wireless bridge. You will be able to effortlessly transfer files. In addition, you're equipped to share an internet connection, and even play multiplayer games. So, give it a try and experience the convenience. What seemed like a challenge is now a straightforward solution. Consequently, you can enjoy the interconnectedness between your laptop and PC. So, embrace the simplicity of ad-hoc networking!
Dell Laptop WiFi Nightmare? Solved!Laptop to PC WiFi: Windows 7 Secret Trick Revealed!
Alright, tech enthusiasts and Windows 7 survivors (yes, you!), let's dive headfirst into a problem that's plagued many of us: getting your beloved laptop to share its Wi-Fi with your desktop PC. Remember those days when you had to physically move your laptop around, hoping for a strong signal, or worse, run an Ethernet cable across the living room like a digital vine? We've all been there! But fear not, because we're about to crack a secret, a hidden gem within the depths of Windows 7 that will liberate your desktop from the tyranny of wired connections. This isn't a tech wizard's secret, but a clever workaround that's surprisingly simple.
Unveiling the Mystery: Why Share Your Laptop's Wi-Fi?
Before we dive into the how, let's talk about the why. Why would you even want to share your laptop's Wi-Fi? Well, think about it. Maybe your desktop PC is stuck in a corner of your house that's a Wi-Fi dead zone. Or, perhaps your primary internet connection isn't working, but your laptop, miraculously, has a strong signal. It could be that you want to save the hassle of running a long Ethernet cable, turning your home into a digital obstacle course. Whatever the reason, the ability to share your laptop's wireless connection with your desktop PC is a total game-changer. It’s like having a portable hotspot that you can strategically place where you need it most.
The Windows 7 Hidden Feature: Ad-Hoc Networks - The Secret Weapon
The secret sauce, the hidden trick, the magic bullet (okay, I’ll stop with the metaphors!) is Windows 7’s built-in ability to create an "Ad-Hoc" network. Think of it as a tiny, private Wi-Fi network created specifically for connecting devices directly to each other. It's like your laptop becomes a mini-router, broadcasting its internet connection for your desktop to receive. The best part? This feature is already built into Windows 7; you just need to know where to find it and how to use it.
Step-by-Step Guide: Turning Your Laptop into a Wi-Fi Bridge
Let's get down to brass tacks and get your desktop PC online. Here's a straightforward guide to setting up your laptop as a Wi-Fi bridge:
Step 1: Accessing Network and Sharing Center
First things first, we need to head to your Network and Sharing Center. You can typically find this by clicking on the network icon (the little computer screen) in the system tray, down in the bottom right corner of your screen. Then, click on "Open Network and Sharing Center."
Step 2: Creating an Ad-Hoc Network
In the Network and Sharing Center, look for the option to "Set up a new connection or network." Click on that, and then select "Set up a wireless ad hoc (computer-to-computer) network."
Step 3: Configuring Your Ad-Hoc Network
A window will pop up, guiding you through the setup. You'll need to give your network a name (choose something memorable!) and select a security type; WPA2-Personal is generally recommended for security. You also need to create a password. Think of these credentials as your digital key; keep it private and secure!
Step 4: Sharing Your Internet Connection (The Crucial Step!)
Once your Ad-Hoc network is created, it’s time to share your laptop's internet connection. Go back to the Network and Sharing Center. You'll see your laptop's current Wi-Fi connection listed. Right-click on it, and select "Status." Then, click on "Wireless Properties," head to the "Sharing" tab, and check the box that says "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection." Underneath, in the "Home networking connection" dropdown, select the name of your Ad-Hoc network that you created in Step 3. Click "OK," and you're all set!
Step 5: Connecting Your Desktop PC to the Ad-Hoc Network
On your desktop PC, search for available Wi-Fi networks. You should see the network name you created in Step 3. Select it, enter the password you established, and connect. Voila! Your desktop should now be connected to the internet, courtesy of your laptop's Wi-Fi.
Troubleshooting Common Roadblocks
Let's be honest, tech isn't always smooth sailing. Sometimes, you might run into a few bumps in the road. Here are a few common issues and how to address them:
- Connection Issues: Double-check the password you entered on your desktop. Make sure your laptop's Wi-Fi is actually connected to the internet. Restarting both your laptop and desktop can often work wonders.
- Slow Speeds: Ad-hoc networks aren't always the fastest, but the speed should be adequate for basic browsing and email. Consider your laptop's Wi-Fi strength and proximity to the router.
- Security Concerns: Remember to use a strong password for your Ad-Hoc network to prevent unauthorized access.
Windows 7's Legacy: A Nod to the Past
It's worth acknowledging that Windows 7 is now officially "end of life," meaning Microsoft no longer provides security updates. While this trick still works, you should consider upgrading to a newer operating system for better security and ongoing support. However, for those clinging to their trusty Windows 7 machines, this trick is a useful solution.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Your Ad-Hoc Network's Performance
Want to squeeze every ounce of performance out of your Ad-Hoc network? Here are a few tips:
- Placement: Place your laptop in a location that receives a strong Wi-Fi signal. The closer, the better.
- Interference: Avoid placing your laptop near devices that could interfere with the Wi-Fi signal, such as microwaves or cordless phones.
- Limited Devices: The more devices connected to your Ad-Hoc network, the slower the connection will be. If possible, only connect your desktop PC.
The Future of Connectivity: What's Next?
While Ad-Hoc networks in Windows 7 are a clever solution, they're definitely "old school." Modern operating systems and routers offer more seamless and secure ways to share your internet connection, such as Wi-Fi Direct or using your smartphone as a mobile hotspot. But for those of us still using Windows 7, this is a solid, reliable method, and it does the trick.
Windows 7 vs. Modern Day: A Quick Comparison
Let's take a bird's-eye view and compare Windows 7’s method with how things work nowadays.
- Windows 7 Ad-Hoc: Requires specific steps, lower security (when considering the OS's age), and can be less user-friendly.
- Modern Wi-Fi Sharing: Often built-in to the OS, easier to set up, and uses modern security protocols.
The Human Element: Why This Still Matters
Why are we discussing Windows 7 and a potentially outdated feature? Because we all have those moments when we need a quick solution, a temporary fix, or an emergency connection. And sometimes, the old ways are the best ways! This solution gets you online, and that’s what matters.
Personal Anecdotes: My Own Windows 7 Wi-Fi Adventures
I remember a time when my primary router conked out during a critical work deadline. Without this Windows 7 trick, I would have been dead in the digital water!
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Simplicity
So there you have it! A hidden Windows 7 feature that may save you the hassle of cables, or may even save you from a connectivity debacle. Isn't it amazing how even older technology packs a powerful punch?
The Elegance of Simplicity in Tech: Wrapping it Up
We've explored a simple solution for a common problem: connecting your desktop PC to Wi-Fi using your laptop in Windows 7. It's a bit of a retro trick, sure, but it is a solid reminder that even older systems can still be surprisingly effective.
FAQs: Your Burning Questions Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions to clear up any lingering doubts:
- Will this work with Windows 10 or 11? No, the method for setting up an Ad-Hoc network is much different (and the feature is often disabled by default) in newer Windows versions. However, newer versions have more straightforward ways to share Wi-Fi.
- Is it secure? Use a strong password for your Ad-Hoc network. Also, be aware that Windows 7 is no longer receiving security updates, so there are inherently some security risks.
- What if it doesn't work? Double-check all the steps. Restart both devices. Ensure your laptop has a working internet connection. If persistent problems occur, consider upgrading to a more modern operating system.
- Is this faster than a wired connection? Typically, a direct Ethernet connection is faster, but the speed will still be sufficient for many tasks.
- Can I use this to connect more than one device to the internet? Yes but expect the speed to decrease.
Principal Keywords: Laptop PC Wifi Windows 7 Trick
SEO Headline: Laptop to PC Wi-Fi
HP Laptop Hotspot? Unlock FREE WiFi NOW!How to enable your network connection in Windows 7
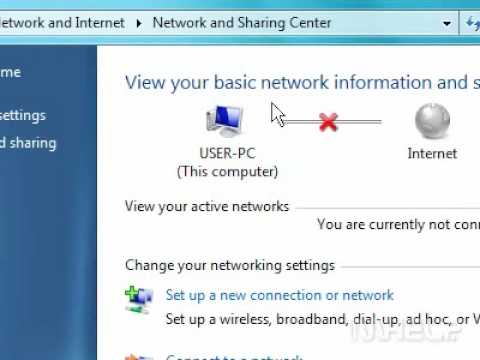
By MHELP2U How to enable your network connection in Windows 7 by MHELP2U
Windows 1110 - How to create a local network and share files between computers over the network

By ipMalik Windows 1110 - How to create a local network and share files between computers over the network by ipMalik
You Are Not Connected to Any Network Fix WiFi
By asal ngelik You Are Not Connected to Any Network Fix WiFi by asal ngelik
Title: Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop
Channel: IT Magics
Windows was unable to connect wifi windows 7 Laptop and Desktop by IT Magics
Wifi Not Found
Laptop to PC WiFi: Windows 7 Secret Trick Revealed!
Navigating the digital landscape often demands seamless connectivity. Whether it's transferring crucial documents, sharing multimedia, or simply extending your internet reach, the ability to connect a laptop to a PC via WiFi becomes exceptionally vital. However, the process of setting up this connection can sometimes feel convoluted, especially for those not intimately familiar with the intricacies of networking. What if we told you there's a straightforward, often overlooked method that simplifies the process, particularly for those still utilizing the robust and reliable Windows 7 operating system? Consider this your comprehensive guide, designed to demystify the connection process and equip you with the knowledge to effortlessly link your laptop and PC via WiFi.
Understanding the Fundamentals: WiFi and the Ad-hoc Connection
Before delving into the "secret trick," it's essential to establish a foundational understanding. WiFi, or Wireless Fidelity, operates through radio waves, enabling devices to communicate without the physical constraints of cables. The method we'll explore leverages an ad-hoc network. Think of an ad-hoc network as a direct, peer-to-peer connection between two devices. Contrary to a typical infrastructure network, that requires a router or access point, an ad-hoc network allows two devices to connect directly, creating their own "mini-network." This is specifically what we'll be using to connect your laptop to your PC.
Step-by-Step Guide: Setting Up the Ad-hoc Network on Your Windows 7 PC
The core of the "secret trick" lies in creating and configuring an ad-hoc network on your Windows 7 PC. This isn't a complex procedure; it's a matter of understanding the steps and applying them accordingly. We will walk you through each step one at a time.
Accessing the Network and Sharing Center: Begin by navigating to your Windows 7 desktop. Locate the system tray, typically found in the lower right corner of your screen. Look for the network icon, which resembles a small computer screen with a signal bar above it. Right-click on this icon, and select "Open Network and Sharing Center."
Creating a New Ad-hoc Network: Within the Network and Sharing Center window, look for the "Set up a new connection or network" option under the "Change your networking settings" heading. Click on this option. This will launch the "Choose a connection option" window. Scroll through the choices and choose "Set up a wireless ad-hoc (computer-to-computer) network." Then click "Next".
Network Configuration: Naming and Security After selecting the ad-hoc network setup option, you'll be prompted to configure the network. The "Set up a wireless ad-hoc network" screen will appear. This is the point where you define the essential parameters of your network.
- Network Name (SSID): Assign a unique and easily recognizable name to your network. This is the name your laptop will see when searching for available WiFi networks. Think of something simple but memorable, such as "MyPCWiFi," or "LaptopLink."
- Security Type: Choose a security type. In the dropdown menu, you'll have a few options. For optimal security (though Windows 7's encryption capabilities are outdated), select "WPA2-Personal." It's generally the most robust of the available choices.
- Security Key: Create a strong, complex password for your network. This password will be required for any device to connect to your ad-hoc network. This key should be at least 8 characters long, and should include a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Write this down somewhere safe, as you'll need it again.
- Save This Network: Ensure the box labeled "Save this network" is checked. By clicking this, Windows will remember the configuration and automatically make the network available.
- Click "Next" to confirm your settings.
Enabling Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) (Optional, but Recommended): In most cases, your Windows 7 PC likely has an existing internet connection, usually via an Ethernet cable or a separate WiFi connection. To allow your laptop to access the internet through your PC's connection, you'll need to enable Internet Connection Sharing (ICS).
- Return to the Network and Sharing Center.
- Click "Change adapter settings."
- Identify the network adapter that is currently connected to the internet (e.g., Ethernet or WiFi). Right-click on that adapter and select "Properties."
- Click on the "Sharing" tab.
- Check the box labeled "Allow other network users to connect through this computer's Internet connection."
- In the "Home networking connection" dropdown menu, select the ad-hoc network you just created.
- Click "OK" to save the settings.
Network Readiness: Your Windows 7 PC is now set up to act as a WiFi hotspot. The next step is to connect your laptop.
Connecting Your Laptop: Joining the Ad-hoc Network
With your Windows 7 PC configured, the next step is to connect your laptop to the created ad-hoc network.
Searching for Available Networks: On your laptop, look for the WiFi icon in the system tray, near the clock. Click on it to display a list of available WiFi networks.
Selecting Your Ad-hoc Network: Locate the network name (SSID) you created on your PC (e.g., "MyPCWiFi" or "LaptopLink") in the list. Select it.
Entering the Security Key: You will be prompted to enter the security key (password) that you set up during the PC configuration. Type in the correct password and click "Connect."
Connection Verification: Once connected, your laptop should display a confirmation message. Verify that are connected by checking your network status in the system tray or through the network settings.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Even with a precise understanding of the steps, connection issues occasionally arise. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Unable to see the Ad-hoc Network:
- Ensure the ad-hoc network is actively broadcasting from your PC. Check that the WiFi adapter on your PC is enabled.
- Check if your laptop's Wi-Fi adapter is enabled.
- Make sure the network name (SSID) is entered correctly on the laptop.
- Incorrect Security Key: Double-check the password you are entering on the laptop. The password is case-sensitive.
- Internet Access Problems (if ICS is enabled):
- Verify that the ICS settings are properly configured on your PC's internet connection adapter.
- Ensure Windows Firewall isn't blocking the connection. Temporarily disabling the firewall can help determine if it's the cause.
- Restart both your PC and laptop, and then try reconnecting.
- Conflicting IP Addresses: Rarely, your PC and laptop might receive conflicting IP addresses. Windows usually handles this automatically, but if you encounter issues, you can manually assign static IP addresses within the same subnet (e.g., 192.168.1.x for the PC and 192.168.1.y for the laptop, where x and y are unique numbers from 2 to 254).
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Tips and Considerations
Mastering the basic connection is one thing, but extending your capabilities can truly unlock the full potential of this connection method.
- File Sharing: Once connected, you can easily share files between your PC and laptop. Enable file and printer sharing in your Windows 7 settings and set up shared folders. From your laptop, you can then browse and access files on your PC.
- Printer Sharing: If your PC has a connected printer, you can share it with your laptop. Go to your PC's "Devices and Printers" section in the Control Panel, right-click on the printer, and select "Printer properties." Go to the "Sharing" tab, and check the box to share the printer. Then, on your laptop, add the network printer using the PC's IP address or computer name.
- Security Best Practices: While the WPA2-Personal security is adequate, always ensure that firmware on your WiFi adapters is up-to-date to patch any security vulnerabilities. Be mindful of the data you transfer over an unsecured network; avoid transmitting sensitive information.
- Considerations for Newer Operating Systems: While this guide focuses on Windows 7, the core principles also apply to more recent operating systems. The steps may vary slightly, but the concept of an ad-hoc network remains consistent across Windows versions.
- Alternatives to Ad-hoc: If security is a primary concern, or if your PC has a built-in WiFi adapter, a more robust option might be to use your PC as a WiFi hotspot via the built-in capabilities of newer Windows versions. This typically involves setting up a "mobile hotspot" using the WiFi adapter on your PC. These methods often offer better security and connection stability. You can search online for "Windows 10/11 Hotspot setup," for example.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of the Secret Trick
By mastering the art of connecting your laptop to your PC via WiFi using the often-overlooked ad-hoc method, you unlock a world of seamless connectivity and data transfer capabilities. Whether you're a student, a professional, or
