cara mempercepat koneksi wifi laptop windows 8
Title: Cara Mempercepat Koneksi Jaringan Wifi Di Laptop
Channel: Wira HK
Cara Mempercepat Koneksi Jaringan Wifi Di Laptop by Wira HK
**Windows 8 WiFi Speed: SHOCKING Trick to Get Blazing Fast Speeds!**
Unleash the Beast: Windows 8 WiFi Speed Secrets Revealed!
Okay, buckle up buttercups! You're about to enter a world of Wi-Fi wizardry. Are agonizingly slow internet speeds making you want to chuck your laptop out the window? It's a common plight, especially when we're talking about the aging Windows 8. But hold your horses. Before you resign yourself to buffering hell, listen up. There's a secret weapon. This isn't some dusty, tired old trick. You could be experiencing blazing-fast speeds right now!
The WiFi Woes of Windows 8: A Frustrating Reality
Let’s be honest. Windows 8, despite its innovations, sometimes feels like a relic. Its Wi-Fi performance can be, well, let's say less than optimal. Consider your frustration. You’re staring at a loading progress bar. Pages struggle to load. Streaming videos stutter and freeze. This is the reality for many Windows 8 users. However, it doesn't have to be yours.
Diagnosing the Digital Slowdown: Pinpointing the Culprit
Before we jump into the fix, let's be detectives. First, is the issue your network? Is it your router? Is it your internet plan? Perhaps the problem is the distance between your device and the router. Alternatively, other devices on the network may be hogging all the bandwidth. Sometimes, the culprit is simply outdated drivers. Once you’ve ruled those out, start here.
The Hidden Gem: Unveiling Driver Secrets
Believe it or not, this is where the magic resides. The secret to unlocking your Windows 8 Wi-Fi potential? It's all about the drivers. Drivers are essentially the communication link between your hardware (your Wi-Fi adapter) and your operating system (Windows 8). Now, because Windows 8 is older, outdated drivers are a massive issue. Thus, the best way to improve your speed is to update them.
Step-by-Step to WiFi Enlightenment: Driver Update Tactics
Ready to transform your internet speed? Here’s how:
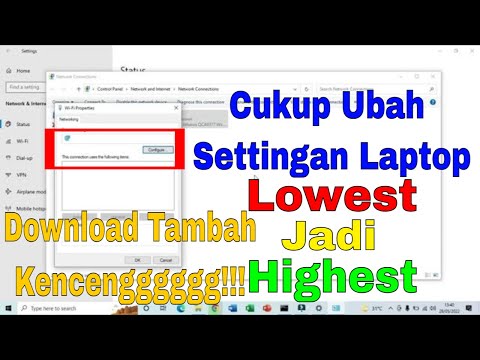
- The Device Manager Dive: Click the Windows key + R (the "Run" box). Type "devmgmt.msc" and hit Enter. It’s your gateway to hardware management.
- Network Adapter Hunt: In the device manager, look for "Network Adapters." Expand this section. You'll see your Wi-Fi adapter listed, likely with a generic name.
- The Right-Click Revelation: Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter. Then, select "Update driver."
- Automatic vs. Manual: Choose Wisely: You have two choices. Select "Search automatically for drivers" (Windows will try to find the latest). If that doesn't work immediately, explore the "Browse my computer for driver software" option.
- Manual Driver Search: Sometimes, Windows fails with the auto search. In that scenario, you might need to locate the driver manually. This usually means visiting your computer manufacturer's website (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) and downloading the specific driver for your Wi-Fi adapter and Windows 8 version.
- Install and Restart: Follow the on-screen prompts to install the driver. Then, restart your computer. This is crucial!
Beyond the Basics: Tweaking for Maximum Velocity
Now let's go a step further. After updating your drivers, there might be additional tweaks.
- Power Management: Go back to Device Manager. Right-click the Wi-Fi adapter. Select “Properties.” Then, go to the “Power Management” tab. Uncheck the box that allows the computer to turn off the device to save power. This is a classic speed booster.
- Router Proximity: The closer you are to your router, generally the better.
- Channel Optimization: Log into your router’s settings. Change the wireless channel. Experiment with different channels to find the least congested one. Research which channels are best for your region.
- Isolate Interference: Move your router away from microwaves, cordless phones, and other sources of interference.
Troubleshooting Troubles: What to Do If Things Go Wrong
So, what if things don't go as planned? Don't panic! Here's a troubleshooting checklist:
- Roll Back the Driver: If the new driver creates problems, revert to the previous one. In Device Manager, right-click the adapter, select "Properties," go to the "Driver" tab, and click "Roll Back Driver."
- Reinstall the Driver: Sometimes, a fresh install cures the issue. Uninstall the driver in Device Manager and then reinstall it using the steps above.
- Check Your Internet Connection: Is your internet actually working, in general? Test the internet using a different device (like your phone) to see if your problem stems from outside issues.
- Consult the Experts: When all else fails, find professional technical support.
The Verdict: Embrace the Speed!
Once you follow these steps, you should experience a noticeable boost in your Windows 8 WiFi speeds. It might not be a complete transformation, but you will likely experience a significant improvement. Enjoy the smoother streaming, the faster downloads, and the generally better online experience. With a little effort, you can still make Windows 8 sing. After all, isn't an upgraded internet experience worth the effort? Happy browsing.
Phone to Laptop: Wireless Data Transfer - The SHOCKINGLY Easy Way!Windows 8 WiFi Speed: SHOCKING Trick to Get Blazing Fast Speeds!
Hey everyone, it's me again! Ever felt like your Windows 8 laptop was stuck in dial-up mode while everyone else is zipping around on the information superhighway? You're trying to stream your favorite show, but instead, you're getting the dreaded buffering wheel of doom? Or maybe you're trying to download a file that's taking longer than the release of the next Lord of the Rings movie? Yeah, we've all been there. The frustration is real, and it's enough to make you want to throw your laptop out the window (metaphorically, of course!). But before you reach for the ejection button, let's talk about a sneaky little secret – a SHOCKING trick – that could seriously boost your Windows 8 WiFi speed! Seriously, it's like breathing new life into an old horse. Let's dive in!
1. The WiFi Woes of Windows 8: Why Is It so Slow?
First things first: why is your Windows 8 WiFi potentially dragging its virtual feet? Well, there are a few usual suspects. A common culprit is outdated network drivers. Think of it like this: your network card is the car, and the drivers are the GPS. If the GPS is outdated, you might end up taking the scenic route… every single time! Then there's the inherent age of the hardware. Windows 8 is getting on in years, and the WiFi cards of that era might not be the fastest kids on the block, especially when dealing with modern WiFi standards. Think of it like comparing a classic muscle car to a Formula 1 racer. The muscle car is cool, but it's not winning any races against the latest technology. Finally, you could be dealing with network congestion. The more devices connected to your router, the slower the speed for each individual device, like a busy highway during rush hour.
2. Unveiling the SHOCKING Trick: The Power Management Gambit
Alright, drumroll, please… the SHOCKING trick is all about your power management settings! Don't let the name fool you; it's not just about saving battery. It's about optimizing your WiFi card's performance. Windows, by default, sometimes tries to conserve power by throttling down your WiFi card when it's running on battery or even when plugged in. This can result in slower speeds. We are going to take control of these settings!
3. How to Access Your Network Adapter Settings
Okay, let's get our hands dirty. Here's how to access your network adapter settings in Windows 8:
- Step 1: Open Device Manager. Right-click on the Start button (or press Windows key + X). Then, select "Device Manager."
- Step 2: Expand Network Adapters. In the Device Manager window, find the "Network adapters" section and click the little arrow to expand it. You should see a list of your network adapters, including your WiFi card.
- Step 3: Right-Click Your WiFi Card. Right-click on your WiFi adapter (it might have a name like "Wireless Network Adapter" or a specific brand like "Intel Wireless").
- Step 4: Select Properties. From the context menu, choose "Properties."
4. Deep Dive: Power Management Settings Unlocked!
Now that you're in the properties window for your WiFi adapter, let's get to the good stuff: the power management settings.
- Step 1: Navigate to the "Power Management" Tab. Click on the "Power Management" tab. You should see a checkbox labeled "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power."
- Step 2: Uncheck the Box! This is the magic bullet. Uncheck this box. This forces your WiFi card to remain awake and active, potentially boosting its performance.
- Step 3: Click "OK" and Restart. Click "OK" to save your changes. Then, restart your computer.
5. Checking Your WiFi Speed Before and After: The Speed Test
Before you make any changes, it's always a good idea to check your current WiFi speed. There are plenty of free online speed test tools available. Use one like Speedtest.net or Fast.com to measure your download and upload speeds. Do this before applying the power management tweak. Then, after restarting your computer, run the speed test again and compare the results. You might be surprised by the difference!
6. Beyond Power Management: Other Factors Impacting WiFi Speed
While the power management trick can be a game-changer, other factors can still affect your WiFi speed. Let's explore those.
7. Driver Updates: Keeping the GPS Up-to-Date
As mentioned earlier, outdated drivers can seriously slow down your WiFi. Make sure your network adapter drivers are up-to-date. You can often update them through Device Manager:
- Step 1: In Device Manager, right-click on your WiFi adapter.
- Step 2: Select "Update driver."
- Step 3: Choose to search automatically for updated driver software. Windows will try to find and install the latest drivers.
8. Router Positioning & Interference: Finding a Sweet Spot
Your router's location matters! Avoid placing it near physical obstacles such as walls, metal objects, and other electronics. Try to place it in a central location in your home for better signal coverage. Also, interference from other devices, like microwaves and cordless phones, can degrade your WiFi signal.
9. Channel Optimization: Finding the Least Congested Lane
Your router broadcasts on a specific WiFi channel. If many other routers in your area are using the same channel, it can lead to congestion. Log into your router's settings (usually through a web browser) and look for the option to change the WiFi channel. Experiment with different channels to find the one with the least interference.
10. Bandwidth Blues: 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz
Many modern routers broadcast on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band offers wider range, but it's often more congested. The 5 GHz band provides faster speeds and less interference, but it has a shorter range. If your Windows 8 laptop and router support 5 GHz, try connecting to that band if you're close enough to the router.
11. Network Adapter Settings: The Advanced Tab
Dive a step further. In the properties window for your WiFi adapter (back in Devise Manager, steps 3-4), go to the "Advanced" tab. Here, you'll find settings specific to your network adapter. You might find options to increase the transmit power or change the wireless mode. Be cautious when tinkering with these settings, and always read the descriptions carefully before making changes.
12. The Router Reset: A Fresh Start
Sometimes, a simple reset of your router can fix WiFi issues. Unplug your router for 30 seconds, then plug it back in. Allow it a few minutes to boot up and reconnect to the internet.
13. Security Protocols: Keeping Your Connection Safe
Make sure your WiFi is using a secure encryption protocol like WPA2 or WPA3. This helps protect your network from unauthorized access. Older protocols like WEP are easily crackable.
14. Troubleshooting Tips: When Things Go Wrong
If you're still experiencing slow WiFi speeds, try these troubleshooting tips:
- Restart your computer and router. It seems basic, but rebooting often solves the problem.
- Check your internet service provider (ISP). Your internet speed might be slow, regardless of your WiFi.
- Run the Windows Network Troubleshooter. Windows has a built-in troubleshooter that can automatically diagnose and fix common network problems.
- Contact your ISP. If all else fails, contact your internet provider. They can provide further assistance or diagnose any problems on their end.
15. The Ultimate WiFi Speed Checklist for Windows 8
Let's recap with a checklist of things to try:
- ✅ Power Management: Uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power" in your WiFi adapter properties.
- ✅ Driver Updates: Ensure your network adapter drivers are up-to-date.
- ✅ Router Placement: Position your router centrally and away from interference.
- ✅ Channel Optimization: Experiment with different WiFi channels.
- ✅ Band Selection: Connect to the 5 GHz band if available and close to the router.
- ✅ Router Reset: Reboot your router.
- ✅ Security: Use a secure encryption protocol like WPA2 or WPA3.
Closing Thoughts: Say Goodbye to Buffering!
There you have it! Hopefully, these tips and tricks, especially the SHOCKING power management trick, will help you get those blazing-fast WiFi speeds you deserve on your Windows 8 laptop. Remember, technology can be a bit like a puzzle. Sometimes, the solution is something simple, like changing your power management settings. So go forth, test, and hopefully, say goodbye to buffering and hello to smooth streaming and faster downloads. Happy browsing!
- Principal Keywords: Windows 8 WiFi Speed Boost
- SEO Headline: Windows 8 WiFi
Cara Mempercepat Sinyal Wifi Laptop Di Windows 1087 Tutorial

By MDTechVideos Cara Mempercepat Sinyal Wifi Laptop Di Windows 1087 Tutorial by MDTechVideos
Cara Mempercepat Jaringan WIFI di LaptopPC TERBARU

By LOBARON Cara Mempercepat Jaringan WIFI di LaptopPC TERBARU by LOBARON
Cara Mempercepat Kinerja Windows 88.1 Yang Lemot

By Teckfo Computer Cara Mempercepat Kinerja Windows 88.1 Yang Lemot by Teckfo Computer

Title: Cara Memperkuat Penangkapan Sinyal Wifi di Laptop
Channel: Sobat OPS
Cara Memperkuat Penangkapan Sinyal Wifi di Laptop by Sobat OPS
My Laptop Work
Here is the title you should write the article for: "The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Photography Lens for Your Needs"
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Photography Lens for Your Needs
The world of photography is vast and vibrant, a tapestry woven with light, shadow, and an endless array of perspectives. At the heart of capturing these moments lies the lens – the window through which we perceive and record the world. Choosing the right lens can feel daunting, given the sheer variety available. However, a deeper understanding of lens types, focal lengths, and their respective applications can empower you to make informed choices, enhancing your creative capabilities and bringing your photographic vision to life. This comprehensive guide will serve as your compass, navigating you through the intricacies of lens selection and helping you discover the perfect tools for your photographic journey.
Understanding the Basics: Focal Length and Aperture
Before diving into specific lens types, it's essential to grasp two fundamental concepts: focal length and aperture. These are the building blocks upon which all lens choices are predicated.
Focal Length: Measured in millimeters (mm), focal length determines the angle of view and magnification. A shorter focal length (e.g., 14mm) offers a wider angle of view, ideal for capturing expansive landscapes or interiors. Conversely, a longer focal length (e.g., 200mm or more) provides a narrower angle of view and greater magnification, perfect for wildlife photography or distant subjects. The focal length also influences perspective; wider lenses tend to exaggerate the distance between objects, while telephoto lenses compress it.
Aperture: Represented by an f-number (e.g., f/2.8, f/16), aperture controls the amount of light that enters the camera and affects depth of field. A wider aperture (smaller f-number, like f/2.8) lets in more light, creating a shallow depth of field – blurring the background and isolating the subject. A narrower aperture (larger f-number, like f/16) lets in less light, resulting in a larger depth of field, keeping both the foreground and background in focus. Aperture also influences sharpness; many lenses perform best at a mid-range aperture (e.g., f/5.6 or f/8).
Exploring Lens Categories: A Comprehensive Overview
Now, let's delve into the diverse world of lens categories, each designed to excel in specific photographic scenarios.
1. Wide-Angle Lenses: Capturing Expansive Views
Wide-angle lenses, typically ranging from 14mm to 35mm, are indispensable for capturing sweeping landscapes, architectural interiors, and group shots. Their wide field of view allows you to encompass more of the scene, creating a sense of grandeur and immersion.
- Applications: Landscape photography, architectural photography, real estate photography, street photography (to capture context), and astrophotography.
- Key considerations: Distortion (especially at very short focal lengths), which can cause straight lines to curve; flare and ghosting, which can occur when shooting into the sun; and the need for precise composition to avoid cluttered compositions.
- Specific Examples: 14mm f/2.8 for astrophotography; 24mm f/1.4 for landscapes and low-light environments; 35mm f/1.4 for street photography and environmental portraits.
2. Standard Lenses: The Versatile All-Rounders
Standard lenses typically have a focal length of around 50mm, mimicking the perspective of the human eye. They offer a natural field of view, making them versatile for a wide range of subjects.
- Applications: General photography, portraits, street photography, and everyday shooting.
- Key considerations: They offer a relatively narrow angle of view compared to wide-angle lenses, which means you need to move closer to your subject. They are often very fast (wide apertures) - making them useful in low-light conditions.
- Specific Examples: 50mm f/1.8, an affordable option for beginners; 50mm f/1.4, offering a wider aperture for enhanced subject separation; 50mm f/1.2, providing excellent low-light performance and a very shallow depth of field.
3. Telephoto Lenses: Bringing Distant Subjects Closer
Telephoto lenses, with focal lengths ranging from 70mm to several hundred millimeters, are designed to magnify distant subjects. They're essential for wildlife photography, sports photography, and portraiture.
- Applications: Wildlife photography, sports photography, portrait photography (for compressing perspective), and photographing events.
- Key considerations: Weight and size (they can be bulky and heavy); image stabilization (IS) or vibration reduction (VR) to minimize camera shake, especially at longer focal lengths; and the need for a stable shooting platform (tripod) when shooting in low light or at very long focal lengths.
- Specific Examples: 70-200mm f/2.8, a popular choice for portraits and sports, offering a versatile zoom range; 100-400mm, offering a wider zoom range for wildlife and sports; fixed focal lengths like 400mm f/2.8 or 600mm f/4, for professionals capturing high levels of detail.
4. Macro Lenses: Unveiling the Microscopic World
Macro lenses are specifically designed for extreme close-up photography, allowing you to capture subjects at a 1:1 magnification ratio (life-size on the sensor).
- Applications: Close-up photography of flowers, insects, products, and other small objects.
- Key considerations: Shallow depth of field, requiring precise focusing; the need for good lighting (often with artificial light sources, such as ring flashes) to illuminate the subject; and the potential for camera shake at high magnification.
- Specific Examples: 50mm macro, suitable for smaller subjects and general close-up work; 100mm macro, providing a longer working distance to avoid disturbing insects or other subjects; and 180mm macro, providing even greater working distance.
5. Zoom Lenses: Adaptability and Convenience
Zoom lenses offer a range of focal lengths within a single lens, providing versatility and convenience. However, they often sacrifice some image quality and maximum aperture compared to prime (fixed focal length) lenses.
- Applications: Travel photography, event photography, and any situation where you need to quickly adjust your framing.
- Key considerations: Maximum aperture (often variable); image quality (can vary between zoom lenses); and size and weight.
- Specific Examples: 24-70mm f/2.8, a versatile zoom for general photography; 70-200mm f/2.8, providing a telephoto zoom range for portraits and sports; 18-55mm, a common kit lens offering a wide range for beginners.
6. Prime Lenses: Superior Image Quality and Speed
Prime lenses have a fixed focal length, offering superior image quality, sharpness, and often a wider maximum aperture compared to zoom lenses. They’re often favored by professionals for their excellent performance.
- Applications: Portraits, low- light photography, achieving a shallow depth of field, and situations where maximum image quality is essential.
- Key considerations: The need to physically move to reframe your shots (no zooming); and the potential for a lack of flexibility compared to zoom lenses.
- Specific Examples: 35mm f/1.4 offering a wider perspective and excellent low-light capabilities; 85mm f/1.4 for creating beautifully blurred backgrounds in portraits; and 200mm f/2.8 for sports and wildlife.
Matching the Lens to Your Needs: A Practical Approach
Choosing the right lens involves considering your primary photographic subjects, shooting style, and budget. Here are some practical examples.
- Landscape Photography: Wide-angle lenses (e.g., 16-35mm, 24mm) are essential for capturing expansive vistas. Telephoto zooms (e.g., 70-200mm, 100-400mm) can compress perspective and isolate details within a landscape.
- Portrait Photography: Standard lenses (e.g., 50mm) offer a natural perspective and pleasing bokeh (background blur). 85mm lenses are also popular for portraits, offering a tighter framing and even more impressive background separation.
- Wildlife Photography: Telephoto lenses with long focal lengths (e.g., 400mm, 600mm) are crucial for bringing distant animals closer.
- Street Photography: Standard lenses (e.g., 35mm, 50mm) are ideal for capturing candid moments and the environment.
- Travel Photography: A versatile zoom lens (e.g., 24-70mm, 24-105mm) is a good choice for covering a wide range of subjects and situations.
Beyond the Fundamentals: Advanced Considerations
Beyond the basic lens categories, there are several other factors to consider when making your selection.
- Image Stabilization (IS) or Vibration Reduction (VR): This technology helps to minimize camera shake, particularly crucial when shooting handheld in low light or at longer focal lengths.
- Lens Mount: Ensure the lens is compatible with your camera's mount (e.g., Canon EF, Nikon F, Sony
