laptop detecting wifi but not connecting
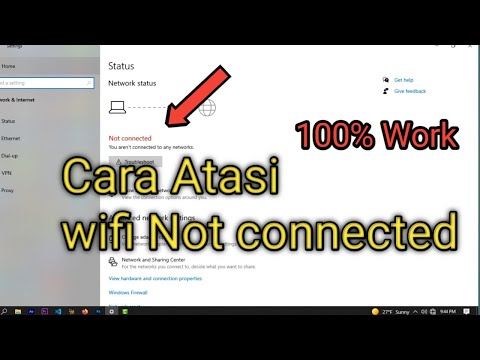
Title: Cara atasi WiFi tidak bisa connect di laptop not connected
Channel: ijal tutorial
Cara atasi WiFi tidak bisa connect di laptop not connected by ijal tutorial
laptop detecting wifi but not connecting windows 10, laptop detecting wifi but not connecting, laptop not detecting my wifi but detecting others
Laptop WiFi: DETECTED but NOT Connecting? FIX IT NOW!
My Laptop Sees the WiFi, But Can't Get Online? Let's Fix That!
Ah, the digital age conundrum. Your laptop sees the WiFi. The signal bars gleam invitingly. Yet, the internet remains elusive. Frustrating, isn't it? You're not alone. This is a common issue. Let's dive into potential solutions. Consider this your troubleshooting guide.
Signal Strength Isn’t Everything: Why Detection Doesn't Equal Connection.
Just because your laptop detects the WiFi doesn't mean it can connect. Think of it like spotting a restaurant. Seeing the sign doesn't guarantee a table. The signal might be weak. Distance can be a factor. Obstacles also matter. Walls and other electronics can interfere. However, detection also means the basics are working. Your wireless card is functioning. It's receiving the signal. The problem lies deeper, usually.
Step 1: Reboot. Really. Yes, Again.
This seems simplistic. However, it frequently works. Restarting your laptop clears temporary glitches. It also refreshes the network connection. Simultaneously, restart your router and modem. Wait a minute or two. Then, try connecting again. Often, this simple act resolves the issue. It’s an easy first test.
Step 2: The Airplane Mode Tango: A Quick Reset
Toggling Airplane Mode is another quick fix. Enable Airplane Mode. Then, disable it. This forces your laptop to search for networks. It re-establishes the WiFi connection. The process is surprisingly effective. It’s like a mini-reset for your wireless card.
Step 3: Checking the Obvious: Is the Password Correct?
We've all been there. You're certain about your password. Double-check it anyway. Typos happen. Case sensitivity matters. Also, ensure Caps Lock isn't on. Sometimes, a small mistake causes a big problem. It’s worthwhile to verify the obvious.
Step 4: Driver Dilemmas: Updating Your Wireless Adapter
Outdated drivers are a frequent culprit. They can cause connectivity issues. To update, go to your Device Manager. You can usually find it by searching in your Windows Start menu. Locate "Network adapters." Expand the list. Then, find your wireless adapter. Right-click it. Select "Update driver." Let Windows search for updates. Alternatively, visit the manufacturer's website. Download the latest driver for your laptop model. Reboot after installation.
Step 5: IP Address Conflicts: A Hidden Battle
IP addresses are crucial. They're how devices communicate. Sometimes, there are conflicts. Resetting your IP settings can help. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator. Type ipconfig /release then press Enter. Then, type ipconfig /renew and press Enter again. Finally, type ipconfig /flushdns. These commands refresh your IP configuration. Restart your computer.
Step 6: Router Reset: A Deeper Dive
If the problem persists, reset your router. There’s usually a small reset button. Press it for about 30 seconds. This will restore your router to its factory settings. You’ll need to re-enter your WiFi password. Make sure to consult your router's manual.
Step 7: Firewall Friction: Checking Your Security Settings
Your firewall might be blocking the connection. Temporarily disable your firewall. Then, try connecting to the WiFi. If it works, your firewall is the problem. You need to adjust its settings. Allow your computer to connect.
Step 8: Physical Positioning: The Signal's Journey
Where you place your laptop matters. Move closer to the router. Sometimes, a few feet make a difference. Minimize obstructions. Remove anything blocking the signal. Experiment with different locations.
Step 9: The Network Troubleshooter: Windows' Secret Weapon
Windows has a built-in troubleshooter. It can often diagnose problems. Search for "Network troubleshooter" in the Start menu. Run the troubleshooter. Let it examine the connection. It often provides helpful suggestions.
Step 10: Last Resort: Contacting Support
If all else fails, seek professional help. Contact your internet service provider (ISP). They can offer further assistance. You can also contact your laptop's manufacturer. Clearly explain the steps you've already tried. They might have specific solutions.
Conclusion: Staying Connected, One Step at a Time
Troubleshooting WiFi is a process. There are many potential causes. Start with the simple solutions. Work your way through the more complex ones. Remember to be patient. You will likely find a solution. Staying connected ensures you stay productive. Ultimately, the goal is a reliable connection. With these steps, you can regain online access quickly. Now get back to browsing!
Is Your Windows 8.1 Laptop Dropping WiFi? This FIX Works Every Time!Laptop WiFi: DETECTED but NOT Connecting? FIX IT NOW!
Alright, fellow tech travelers, let's talk about something that has probably driven us all to the brink of throwing our laptops out the window at some point: Laptop WiFi: DETECTED but NOT Connecting? Ugh! The signal bars are happily beaming, your laptop sees the network, but the internet remains frustratingly elusive. It's like watching a beautiful sunset from behind a locked door – tantalizingly close, yet utterly inaccessible. Fear not, though! We will conquer this digital hurdle. We'll dive deep, get our hands dirty, and emerge victorious, armed with the knowledge to banish those WiFi woes forever (or at least for a good while!).
The WiFi Woes: A Familiar Frustration
Let’s be honest, experiencing this issue can feel like a personal attack on your productivity, your entertainment, and possibly your sanity. You need to check emails, watch that hilarious cat video, or, you know, work? And every time, you’re met with the dreaded "connected, no internet." It’s a common problem, a universal annoyance, and, thankfully, usually quite fixable.
Decoding the Digital Dance: Understanding the Problem
Before we start mashing buttons, let's understand what's happening. Your laptop sees the WiFi network, a bit like recognizing a friend's face, but the handshake – the actual connection – isn't happening. Think of it like this: you're at a crowded party, you see your friend, but you can't actually talk to them. There's a communication breakdown. This can stem from a myriad of factors, ranging from simple software glitches to more complex network issues.
1. The Obvious First Steps: Your Digital "Check Engine" Light
Before we get into the techy stuff, let's address the obvious. I know, I know, you've probably already tried these, but it's always worth checking. Sometimes, the simplest solutions are the best.
- Restart Your Laptop: This is the digital equivalent of "turning it off and on again." It’s a classic for a reason. Restarting clears the cache, refreshes the system, and often solves temporary glitches.
- Restart Your Router and Modem: This is like giving your network a full system reboot. Unplug the modem and router, wait 30 seconds, plug the modem back in, wait for it to fully boot, then plug in the router. This can often reset the communication between your devices and the internet.
- Check the Physical Connections: Ensure your modem and router are properly connected to the wall and each other. Loose wires are a surprisingly common culprit.
2. The Network's Nitty-Gritty: Inspecting Your WiFi Settings
Okay, if the reboots didn't work, let's delve a little deeper into your network settings. We're going into the digital engine room.
- Verify Your WiFi Password: Sounds simple, right? But typos happen! Double-check that you're entering the correct WiFi password. It's easy to miss a capital letter or special character.
- Forget and Reconnect to the Network: This is like clearing the slate. Go into your WiFi settings, find your network, and "forget" it. Then, reconnect as if it's the first time. This can sometimes resolve corrupted network profiles.
3. Driver Dilemmas: Are Your WiFi Drivers Up-to-Date?
Think of drivers as the translators between your laptop and your WiFi adapter. If the translator is broken, communication fails. This is often the root cause of the problem.
- Check Your Device Manager: Go to your laptop's Device Manager (search for it in the Windows search bar). Look for "Network adapters." If you see a yellow exclamation mark next to your WiFi adapter, you have a driver issue.
- Update Your Drivers: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver." Let Windows search automatically. If that doesn't work, you can try downloading the latest drivers from your laptop manufacturer's website. This is like going to the source for the latest instructions.
4. IP Conflicts: The Digital Clashes
Imagine a street where everyone has the same address. Chaos, right? IP addresses are like digital addresses for your devices. Sometimes, two devices on the same network try to use the same address, leading to a conflict.
- Release and Renew Your IP Address: In the Command Prompt (search for "cmd" in the Windows search bar), type
ipconfig /releaseand thenipconfig /renew. This forces your laptop to request a new IP address. - Check Your Router's DHCP Settings: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically assigns IP addresses. Make sure DHCP is enabled on your router.
5. Firewall Frenzies: The Digital Gatekeepers
Your firewall is a security guard, protecting your laptop. Sometimes, it can be too protective, blocking the WiFi connection.
- Temporarily Disable Your Firewall: Disable your firewall briefly to see if it's the cause. (Just remember to re-enable it afterward!). If this fixes the problem, you may need to adjust your firewall settings to allow your laptop to access the internet.
- Check Firewall Exceptions: Make sure your firewall allows internet access for your web browsers and other applications you need to use online.
6. Router Rendezvous: The Router as a Potential Culprit
Sometimes, the problem isn't your laptop, but the router itself.
- Check for Router Firmware Updates: Old firmware can cause connectivity issues. Check your router's admin panel (usually accessible by typing its IP address, found in your router manual, in your web browser) for firmware updates.
- Reset the Router: If all else fails, you might need to reset your router to its factory settings. (Be aware, this will erase your custom settings, so you'll need to reconfigure your network.).
7. Wireless Mode Mischief: Addressing Compatibility Issues
Routers transmit WiFi signals in different modes (like b/g/n/ac). Sometimes, your laptop might not be fully compatible with your router's current mode.
- Adjust Router Wireless Mode Settings: Log in to your router's settings and try changing the wireless mode. Experiment with different modes to see if one works better. Sometimes, switching to a more basic mode, such as 802.11g, can help.
8. Channel Conflicts: the Frequency Fight
WiFi routers broadcast on different channels. If several routers in your neighborhood are using the same channel, it can cause interference.
- Change Your Router's WiFi Channel: Log in to your router's settings and try changing the WiFi channel. There are apps that can help you find the least crowded channel.
9. DNS Drama: Domain Name Server Disconnect
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates website names into IP addresses. If your DNS isn't working, it can prevent you from accessing the internet.
- Change Your DNS Servers: Go to your network adapter properties and manually change your DNS server addresses. You can use public DNS servers like Google's (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare's (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
10. Hardware Hurdles: Addressing the Physical Connection
While rare, sometimes the issue lies with your laptop's WiFi adapter itself.
- Check the Adapter in Device Manager: See if the adapter is disabled. If so, enable it.
- Consider External Adaptors: If the problem persists, you might need to consider getting a USB WiFi adapter to bypass the internal one.
11. Location, Location, Location: Proximity Play
Sometimes, a simple solution is enough. Distance can play a role.
- Move Closer to the Router: WiFi signals weaken over distance. Try moving your laptop closer to the router to see if that improves the connection. Walls and obstructions can also weaken connections,
- Minimize Obstructions: Ensure the router is not hidden. Remove any obstruction that lies between your laptop and the router.
12. The Interference Factor: External Interference
The radio frequencies used for Wi-Fi can also be affected by different devices.
- Limit Nearby Interference: Try moving any device that emits electromagnetic waves farther away from your router. These devices can cause interference.
13. Network Congestion: Addressing Busy Networks
If many devices are using the same network, it can cause congestion.
- Limit Network Usage: Try closing background apps and limiting downloads and streaming during periods of heavy usage.
14. Power Saving Pitfalls: Power Saving Mode
Laptops often employ power saving options that can compromise the WiFi connection.
- Disable Power-saving Mode: Go into your network adapter properties and disable the 'Power saving'. It can cause your WiFi to disconnect.
15. Seeking Expert Assistance: When to Call for Backup
If you've tried all these steps and you're still stuck, it might be time to call in the professionals.
- Contact Your ISP (Internet Service Provider): They can check for issues on their end.
- Take Your Laptop to a Repair Shop: A technician can diagnose hardware problems and provide a lasting solution. A diagnosis might unveil hardware flaws.
Closing Thoughts: You
Unlock ANY WiFi Password with CMD: This Secret Laptop Trick Works!2024 Fix Wi-Fi not working on laptop but working on other devices

By Windows Report 2024 Fix Wi-Fi not working on laptop but working on other devices by Windows Report
7 Ways to Fix a Computer That Can't Find or Connect to Wifi Windows 10 Laptops & Desktops

By Ask A Computer Geek 7 Ways to Fix a Computer That Can't Find or Connect to Wifi Windows 10 Laptops & Desktops by Ask A Computer Geek
Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025
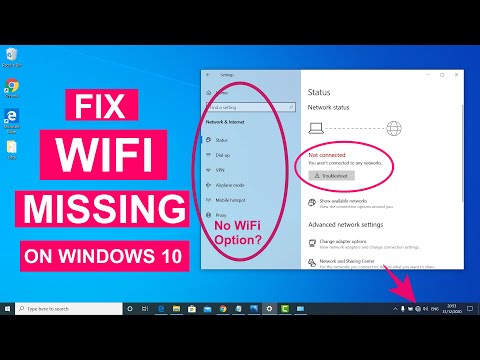
By Sandeep Singh Fix WiFi Not Showing in Settings On Windows 10 Fix Missing WiFi 2025 by Sandeep Singh

Title: How to fix PC not connecting to WiFi
Channel: Scrandalftech
How to fix PC not connecting to WiFi by Scrandalftech
Wifi On Laptop Phone
Laptop WiFi: DETECTED but NOT Connecting? FIX IT NOW!
We’ve all been there: the telltale WiFi icon proudly displaying a full-strength signal, yet the internet stubbornly refuses to cooperate. Your laptop declares a connection, but the web remains frustratingly out of reach. This article dissects the common culprits behind this maddening scenario, offering precise, actionable solutions to get you back online, fast. Forget generic troubleshooting – here, we delve into the specific problems and rigorously tested fixes that truly work.
Confirming the Absence of Internet Activity: A Diagnostic First Step
Before plunging into technical adjustments, establish absolute certainty. The first step is to eliminate ambiguities. Can you access any website, or are you restricted to a specific site that may be down? Attempt to load several different web pages, including major platforms like Google.com, YouTube.com, and your email provider's website. If none of these load, the issue likely resides with your laptop’s WiFi configuration, the router, or your internet service provider (ISP). Conversely, if a site does load, yet others do not, the problem might be site-specific. Also, consider attempting to ping a known website (like google.com) through the command prompt to verify network connectivity at a lower level. This will help you determine whether the problem is with the website or the entire network.
Rebooting Your Arsenal: A Simple but Often Effective Solution
It’s the cliché, but the reboot truly deserves its reputation. Start by restarting your laptop. Then, power cycle your router and modem. Unplug both from their power source, wait a full sixty seconds (allowing capacitors to fully discharge), and then plug the modem back in first. Allow it to fully initialize (indicators should stabilize). Then, plug in the router. Finally, restart your laptop again. This sequence frequently resolves temporary glitches in both your laptop’s WiFi adapter and the network equipment.
Diving into the Wireless Adapter: Drivers and Configurations
The heart of your WiFi connectivity lies in the wireless network adapter. Outdated or corrupted drivers are a frequent cause of connection woes.
Updating Your Network Adapter Drivers
- Access Device Manager: Open the Windows search bar and type "Device Manager." Select the application.
- Locate Network Adapters: Within Device Manager, expand the "Network adapters" section. Here you’ll find your wireless network adapter listed (examples include Intel Wireless-AC 9560 or Realtek RTL8821CE).
- Initiate Driver Update: Right-click on your WiFi adapter and select "Update driver."
- Choose Automatic Search: Select "Search automatically for drivers." Windows will search for and install the latest available drivers.
- Manual Driver Installation: If the automatic update fails, or if you prefer a more proactive approach, you can visit your laptop manufacturer's website (e.g., Dell, HP, Lenovo) and download the latest drivers for your specific model. Install these manually after downloading them.
- Restart for Implementation: After installing or updating the driver, restart your laptop.
Examining and Modifying Network Adapter Properties
Within Device Manager, double-click on your WiFi adapter to open its properties. Here you can adjust specific settings:
- Power Management: Click the "Power Management" tab. Uncheck the box labeled "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power." This prevents Windows from disabling your WiFi adapter to conserve energy, which can interrupt your connection.
- Advanced Settings: Navigate to the "Advanced" tab. Several settings here can impact performance.
- 802.11n/ac Wireless Mode: Select the highest mode your router and adapter support (often "802.11ac" or "802.11n"). A mismatched mode might prevent the connection.
- Channel Width: Experiment with different channel width settings (e.g., 20 MHz, 40 MHz, or Auto).
- Roaming Aggressiveness: Adjust this setting to control how aggressively your laptop seeks out better WiFi signals. A "Medium" or "Low" setting is usually optimal. "Highest" can sometimes cause instability.
- Wireless Mode: Ensure it is set to the standard that is compatible with your router. Mostly, you need to select the highest one that both devices support.
- WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia): Ensure this is enabled, which prioritizes network traffic.
Router-Related Roadblocks: Signal Strength, Compatibility, and Configuration
Your router is the gateway to the internet, and its settings are crucial.
Assessing Signal Strength
A weak signal is a common culprit. Check the WiFi signal strength indicator on your laptop. If the signal bars are low, try moving closer to the router. Walls, furniture, and other electronic devices can interfere with the signal. Also, look for other devices that can disrupt the signal.
Investigating Router Settings
- Access Router Configuration: Open your web browser and enter your router's IP address in the address bar (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). You may need to consult your router’s documentation to find the specific IP address. Enter your username and password (often "admin/admin" or "admin/password"—change this, of course).
- Wireless Network Configuration: Locate the wireless settings. Here are the key configurations to examine:
- Network Name (SSID): Ensure the SSID (the name of your WiFi network) is correct on your laptop.
- Security Type: Verify that the security is enabled and configured correctly (WPA2/WPA3 are the most secure options). Enter your WiFi password correctly.
- Channel: Your router automatically selects a channel; however, interference can occur. Try changing to different channels (1, 6, and 11 are typically the least congested). Experiment with different channels and assess the network performance. Some routers offer an "Auto" setting for channel selection, but manual selection can sometimes resolve connectivity problems.
- Channel Width: Make sure the channel width is set to be compatible with your laptop's network adapter.
- Firmware Updates: Make sure that your router's firmware is up-to-date. Outdated firmware might have security vulnerabilities and performance issues. The firmware is usually updated through the router's administration interface. Go to "Advanced Settings" and seek for a "Firmware Update" options to make sure your router has the most recent update.
Addressing IP Conflicts and DNS Issues: Fine-Tuning Your Network Parameters
Occasionally, problems are not with signal strength or drivers but with how your laptop negotiates with the network.
Troubleshooting with Static IP Addresses
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) automatically assigns an IP address to your laptop. However, IP address conflicts are possible. To avoid this, you can assign a static IP address.
- Open Network Connections: Right-click the WiFi icon in the system tray and select "Open Network & Internet settings."
- Change Adapter Options: Select "Change adapter options."
- Access WiFi Properties: Right-click your WiFi adapter and select "Properties."
- Configure IPv4: Double-click "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)."
- Manual Configuration: Select "Use the following IP address." Then:
- IP Address: Choose an IP address outside your router’s DHCP range. Consult your router settings to discover this range (e.g., 192.168.1.100-192.168.1.200). Select an address outside of this range, such as 192.168.1.250.
- Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask, usually 255.255.255.0.
- Default Gateway: Enter your router’s IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- Preferred DNS Server: Use a public DNS server like Google's (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare's (1.1.1.1).
- Alternate DNS Server: Use Google's (8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare's (1.0.0.1).
- Apply Settings: Click "OK" to save the changes.
Resolving DNS Issues
DNS (Domain Name System) translates website addresses into IP addresses. If your DNS settings are incorrect, websites might fail to load. The method of configuring DNS is provided in the "Static IP Addresses" section.
Security Software Interference: Firewalls and Antivirus Applications
Overzealous security software can sometimes block internet access.
Temporarily Disabling Firewalls
- Open Control Panel: Search for "Windows Defender Firewall" in the Windows search bar, or search for "Firewall" and select it.
- Disable Firewall: Click "Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off" on the left side, then select "Turn off Windows Defender Firewall (not recommended)" for both private and public network settings. Be aware that this is only for troubleshooting and should be re-enabled afterward.
- Test Internet Access: Try accessing the internet. If this resolves the issue, your firewall is
